Page 284 - Earth's Climate Past and Future
P. 284
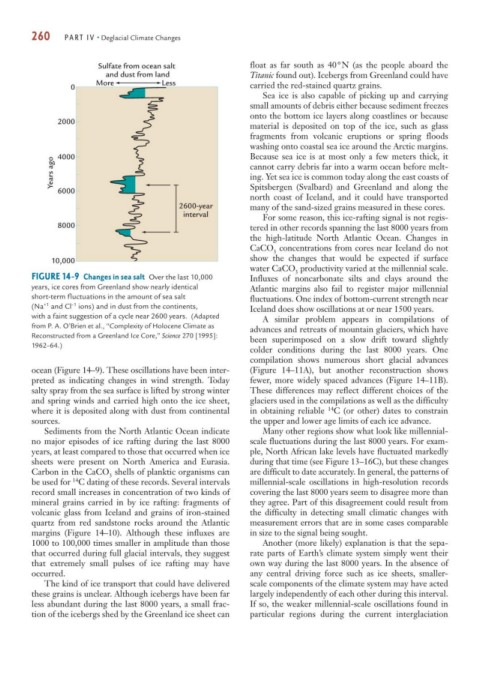
260 PART IV • Deglacial Climate Changes
Sulfate from ocean salt float as far south as 40°N (as the people aboard the
and dust from land Titanic found out). Icebergs from Greenland could have
More Less carried the red-stained quartz grains.
0
Sea ice is also capable of picking up and carrying
small amounts of debris either because sediment freezes
onto the bottom ice layers along coastlines or because
2000
material is deposited on top of the ice, such as glass
fragments from volcanic eruptions or spring floods
washing onto coastal sea ice around the Arctic margins.
4000 Because sea ice is at most only a few meters thick, it
Years ago cannot carry debris far into a warm ocean before melt-
ing. Yet sea ice is common today along the east coasts of
6000 Spitsbergen (Svalbard) and Greenland and along the
north coast of Iceland, and it could have transported
2600-year many of the sand-sized grains measured in these cores.
interval For some reason, this ice-rafting signal is not regis-
8000 tered in other records spanning the last 8000 years from
the high-latitude North Atlantic Ocean. Changes in
CaCO concentrations from cores near Iceland do not
3
10,000 show the changes that would be expected if surface
water CaCO productivity varied at the millennial scale.
3
FIGURE 14-9 Changes in sea salt Over the last 10,000 Influxes of noncarbonate silts and clays around the
years, ice cores from Greenland show nearly identical Atlantic margins also fail to register major millennial
short-term fluctuations in the amount of sea salt fluctuations. One index of bottom-current strength near
–1
+1
(Na and Cl ions) and in dust from the continents, Iceland does show oscillations at or near 1500 years.
with a faint suggestion of a cycle near 2600 years. (Adapted A similar problem appears in compilations of
from P. A. O’Brien et al., “Complexity of Holocene Climate as
advances and retreats of mountain glaciers, which have
Reconstructed from a Greenland Ice Core,” Science 270 [1995]: been superimposed on a slow drift toward slightly
1962–64.)
colder conditions during the last 8000 years. One
compilation shows numerous short glacial advances
ocean (Figure 14–9). These oscillations have been inter- (Figure 14–11A), but another reconstruction shows
preted as indicating changes in wind strength. Today fewer, more widely spaced advances (Figure 14–11B).
salty spray from the sea surface is lifted by strong winter These differences may reflect different choices of the
and spring winds and carried high onto the ice sheet, glaciers used in the compilations as well as the difficulty
14
where it is deposited along with dust from continental in obtaining reliable C (or other) dates to constrain
sources. the upper and lower age limits of each ice advance.
Sediments from the North Atlantic Ocean indicate Many other regions show what look like millennial-
no major episodes of ice rafting during the last 8000 scale fluctuations during the last 8000 years. For exam-
years, at least compared to those that occurred when ice ple, North African lake levels have fluctuated markedly
sheets were present on North America and Eurasia. during that time (see Figure 13–16C), but these changes
Carbon in the CaCO shells of planktic organisms can are difficult to date accurately. In general, the patterns of
3
14
be used for C dating of these records. Several intervals millennial-scale oscillations in high-resolution records
record small increases in concentration of two kinds of covering the last 8000 years seem to disagree more than
mineral grains carried in by ice rafting: fragments of they agree. Part of this disagreement could result from
volcanic glass from Iceland and grains of iron-stained the difficulty in detecting small climatic changes with
quartz from red sandstone rocks around the Atlantic measurement errors that are in some cases comparable
margins (Figure 14–10). Although these influxes are in size to the signal being sought.
1000 to 100,000 times smaller in amplitude than those Another (more likely) explanation is that the sepa-
that occurred during full glacial intervals, they suggest rate parts of Earth’s climate system simply went their
that extremely small pulses of ice rafting may have own way during the last 8000 years. In the absence of
occurred. any central driving force such as ice sheets, smaller-
The kind of ice transport that could have delivered scale components of the climate system may have acted
these grains is unclear. Although icebergs have been far largely independently of each other during this interval.
less abundant during the last 8000 years, a small frac- If so, the weaker millennial-scale oscillations found in
tion of the icebergs shed by the Greenland ice sheet can particular regions during the current interglaciation