Page 287 - Earth's Climate Past and Future
P. 287
CHAPTER 14 • Millennial Oscillations of Climate 263
Climate shielding permitted more bombardment by charged
Colder Warmer 14
cosmic particles (protons) and faster production of C
Younger atoms.
Shorter-term changes in age offsets are also appar-
ent within the last 10,000 years (Figure 14–14). These
1500 Minor ice rafting discrepancies may also reflect changes in the rate of
years production of 14 C atoms in Earth’s atmosphere,
although in this case the main cause is thought to be
changes in emissions from the Sun rather than the over-
print of Earth’s magnetic shielding. Particles streaming
from the Sun (called the solar wind) deflect some of the
incoming cosmic rays (protons) that would otherwise
enter Earth’s atmosphere (Figure 14–15). Changes in
Major ice rafting event the amount of solar deflection over hundreds of years
at multiples of 14
1500 years could alter the C production rate in the atmosphere
and explain the short-term differences in ages derived
from the two dating methods.
14
Older The major cycle of C production in this 10,000-
year record was centered at 420 years, considerably
shorter than the millennial time scale explored in this
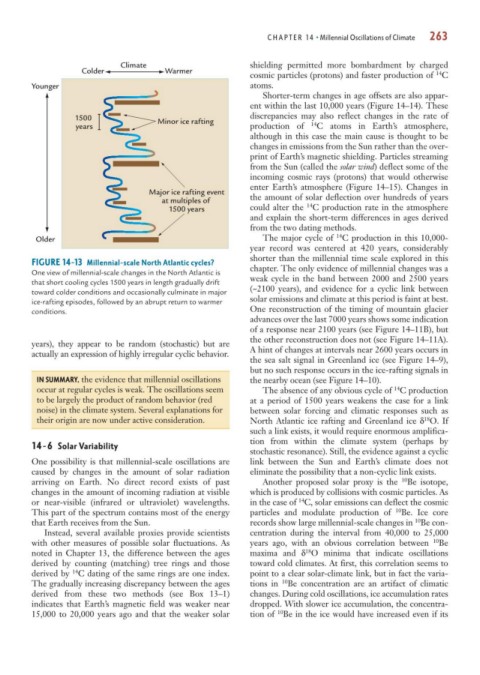
FIGURE 14-13 Millennial-scale North Atlantic cycles? chapter. The only evidence of millennial changes was a
One view of millennial-scale changes in the North Atlantic is
that short cooling cycles 1500 years in length gradually drift weak cycle in the band between 2000 and 2500 years
toward colder conditions and occasionally culminate in major (~2100 years), and evidence for a cyclic link between
ice-rafting episodes, followed by an abrupt return to warmer solar emissions and climate at this period is faint at best.
conditions. One reconstruction of the timing of mountain glacier
advances over the last 7000 years shows some indication
of a response near 2100 years (see Figure 14–11B), but
the other reconstruction does not (see Figure 14–11A).
years), they appear to be random (stochastic) but are
actually an expression of highly irregular cyclic behavior. A hint of changes at intervals near 2600 years occurs in
the sea salt signal in Greenland ice (see Figure 14–9),
but no such response occurs in the ice-rafting signals in
IN SUMMARY, the evidence that millennial oscillations the nearby ocean (see Figure 14–10).
occur at regular cycles is weak. The oscillations seem The absence of any obvious cycle of C production
14
to be largely the product of random behavior (red at a period of 1500 years weakens the case for a link
noise) in the climate system. Several explanations for between solar forcing and climatic responses such as
their origin are now under active consideration. North Atlantic ice rafting and Greenland ice δ O. If
18
such a link exists, it would require enormous amplifica-
tion from within the climate system (perhaps by
14-6 Solar Variability
stochastic resonance). Still, the evidence against a cyclic
One possibility is that millennial-scale oscillations are link between the Sun and Earth’s climate does not
caused by changes in the amount of solar radiation eliminate the possibility that a non-cyclic link exists.
10
arriving on Earth. No direct record exists of past Another proposed solar proxy is the Be isotope,
changes in the amount of incoming radiation at visible which is produced by collisions with cosmic particles. As
14
or near-visible (infrared or ultraviolet) wavelengths. in the case of C, solar emissions can deflect the cosmic
10
This part of the spectrum contains most of the energy particles and modulate production of Be. Ice core
that Earth receives from the Sun. records show large millennial-scale changes in Be con-
10
Instead, several available proxies provide scientists centration during the interval from 40,000 to 25,000
10
with other measures of possible solar fluctuations. As years ago, with an obvious correlation between Be
18
noted in Chapter 13, the difference between the ages maxima and δ O minima that indicate oscillations
derived by counting (matching) tree rings and those toward cold climates. At first, this correlation seems to
derived by C dating of the same rings are one index. point to a clear solar-climate link, but in fact the varia-
14
The gradually increasing discrepancy between the ages tions in Be concentration are an artifact of climatic
10
derived from these two methods (see Box 13–1) changes. During cold oscillations, ice accumulation rates
indicates that Earth’s magnetic field was weaker near dropped. With slower ice accumulation, the concentra-
10
15,000 to 20,000 years ago and that the weaker solar tion of Be in the ice would have increased even if its