Page 33 - Earth's Climate Past and Future
P. 33
CHAPTER 1 • Overview of Climate Science 9
POLES TROPICS
Solar radiation
Greenhouse gases
(CO , CH , H Ov)
2 4 2
Back
radiation
CO Precipitation
2 Evaporation
SO 2
Ice Heat Wind
sheet
Sea ice Carbon Weathering River runoff Sea
production level
Upwelling
CO
2
Carbon
Deep burial
water
Plate motion Uplift
Spreading Subduction
90˚ Latitude 0˚
CAUSES CLIMATE SYSTEM CLIMATE VARIATIONS
(external forcing) (internal interactions) (internal responses)
Changes in Changes
plate tectonics in
Atmosphere Atmosphere
Changes
in
Ice
Changes
Changes in Vegetation Ice in
Earth’s orbit vegetation
Changes
in
Ocean
Land
Changes in surface Ocean Changes in
Sun’s strength land
surface
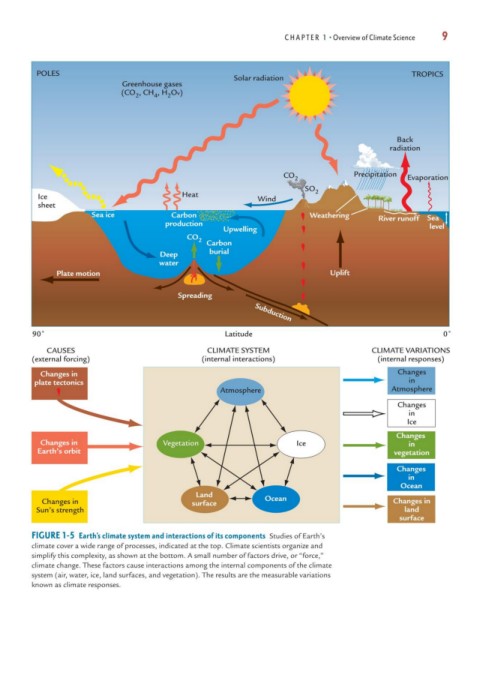
FIGURE 1-5 Earth’s climate system and interactions of its components Studies of Earth’s
climate cover a wide range of processes, indicated at the top. Climate scientists organize and
simplify this complexity, as shown at the bottom. A small number of factors drive, or “force,”
climate change. These factors cause interactions among the internal components of the climate
system (air, water, ice, land surfaces, and vegetation). The results are the measurable variations
known as climate responses.