Page 191 - Educational Technology A Primer for the 21st Century
P. 191
184 11 Design-Based Research
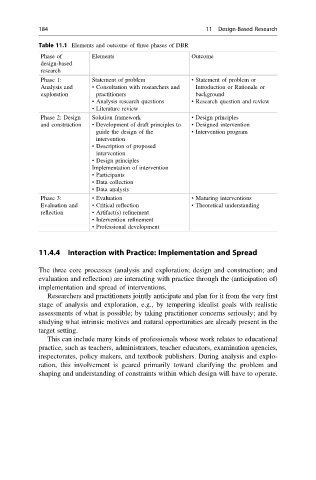
Table 11.1 Elements and outcome of three phases of DBR
Phase of Elements Outcome
design-based
research
Phase 1: Statement of problem • Statement of problem or
Analysis and • Consultation with researchers and Introduction or Rationale or
exploration practitioners background
• Analysis research questions • Research question and review
• Literature review
Phase 2: Design Solution framework • Design principles
and construction • Development of draft principles to • Designed intervention
guide the design of the • Intervention program
intervention
• Description of proposed
intervention
• Design principles
Implementation of intervention
• Participants
• Data collection
• Data analysis
Phase 3: • Evaluation • Maturing interventions
Evaluation and • Critical reflection • Theoretical understanding
reflection • Artifact(s) refinement
• Intervention refinement
• Professional development
11.4.4 Interaction with Practice: Implementation and Spread
The three core processes (analysis and exploration; design and construction; and
evaluation and reflection) are interacting with practice through the (anticipation of)
implementation and spread of interventions.
Researchers and practitioners jointly anticipate and plan for it from the very first
stage of analysis and exploration, e.g., by tempering idealist goals with realistic
assessments of what is possible; by taking practitioner concerns seriously; and by
studying what intrinsic motives and natural opportunities are already present in the
target setting.
This can include many kinds of professionals whose work relates to educational
practice, such as teachers, administrators, teacher educators, examination agencies,
inspectorates, policy makers, and textbook publishers. During analysis and explo-
ration, this involvement is geared primarily toward clarifying the problem and
shaping and understanding of constraints within which design will have to operate.