Page 97 - Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
P. 97
90 Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
FIG. 3.12 Thrust bearings. (A) A thrust bearing based on ball bearing. (B) A thrust bearing based on roller
bearings. In the ball bearing design it is clear that a significant radial load cannot not be constrained, as in the
case of the design based on roller bearings.
Thrust bearing, Fig 3.12A, composed of bearing balls supported in a ring, these can
be used in low thrust applications where there is relatively small axial load, but are
susceptible to radial loads.
Tapered roller thrust bearings, Fig 3.12B, consist of small tapered rollers arranged so
that their axes all converge at a point on the axis of the bearing. Typically, these
bearings are used in pairs to accommodate axial thrust in either direction, as well as
radial loads.
3.4.2 Conventional linear bearings
Many systems that incorporate machine slides, XdY tables, roller tables require the use
of linear bearings. As with rotary bearing, a linear bearing can be based on ball bearings,
linear roller bearings, magnetic or fluid bearings depending on the application.
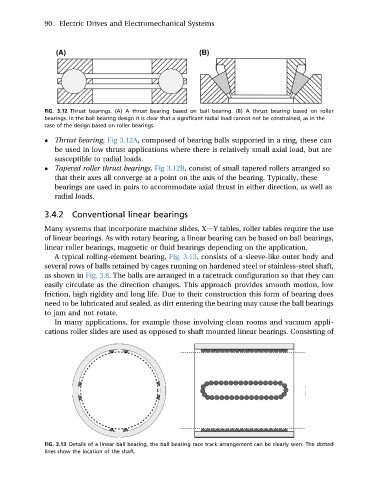
A typical rolling-element bearing, Fig. 3.13, consists of a sleeve-like outer body and
several rows of balls retained by cages running on hardened steel or stainless-steel shaft,
as shown in Fig. 3.8. The balls are arranged in a racetrack configuration so that they can
easily circulate as the direction changes. This approach provides smooth motion, low
friction, high rigidity and long life. Due to their construction this form of bearing does
need to be lubricated and sealed, as dirt entering the bearing may cause the ball bearings
to jam and not rotate.
In many applications, for example those involving clean rooms and vacuum appli-
cations roller slides are used as opposed to shaft mounted linear bearings. Consisting of
FIG. 3.13 Details of a linear ball bearing, the ball bearing race track arrangement can be clearly seen. The dotted
lines show the location of the shaft.