Page 60 - Electric Machinery Fundamentals
P. 60
36 ELECTRIC MACHJNERY FUNDAMENTALS
Switch Magnetic field into page
R B
1 X X X
-=- VB e ind +
X X X
FIGURE 1-19
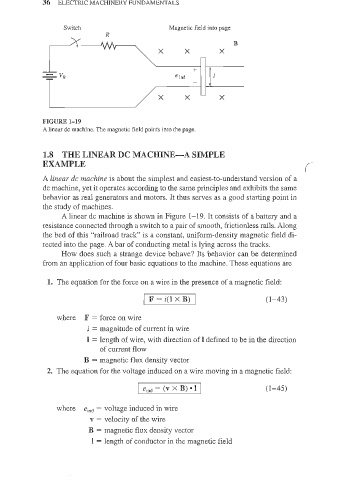
A linear dc machine. The magnetic field points into the page.
1.8 THE LINEAR DC MACHINE-A SIMPLE
EXAMPLE (
A linear dc machine is about the simplest and easiest-to-understand version of a
dc machine, yet it operates according to the same principles and exhibits the same
behavior as real generators and motors. It thus serves as a good starting point in
the study of machines.
A linear dc machine is shown in Figure 1-19. It consists of a battery and a
resistance connected through a switch to a pair of smooth, frictionless rails. Along
the bed of this "railroad track" is a constant, uniform-density magnetic field di-
rected into the page. A bar of conducting metal is lying across the tracks.
How does such a strange device behave? Its behavior can be determined
from an application of four basic equations to the machine. These equations are
1. The equation for the force on a wire in the presence of a magnetic field:
I F = ;(1 X B) I (1-43)
where F = force on wire
i = magnitude of current in wire
I = length of wire, with direction of I defined to be in the direction
of current flow
B = magnetic flux density vector
2. The equation for the voltage induced on a wire moving in a magnetic field:
I e,oct = (v X B) • I I (1-45)
where e inci = voltage induced in wire
v = velocity of the wire
B = magnetic flux density vector
I = length of conductor in the magnetic field