Page 62 - Electric Machinery Fundamentals
P. 62
38 ELECTRlC MACHINERY FUNDAMENTALS
"~~----===
O~,
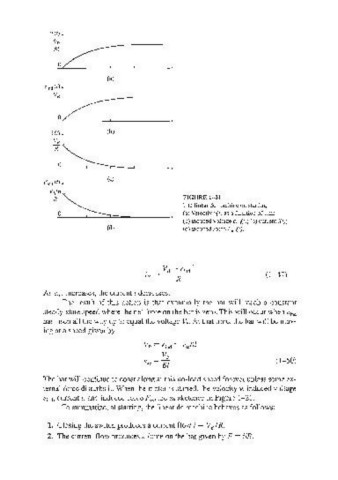
FIGURE 1-21
The linear de machine on i'itmt ing.
(a) Velocity v(r) as a function of time;
(b) induced voltage eind(t); (e) current i(t);
(d) (d) induced force F;nit}.
(1 - 47)
As eind increases, the current i decreases.
The result of this action is that eventually the bar will reach a constant
steady-state speed where the net force on the bar is zero. This will occur when eind
has risen all the way up to equal the voltage VB' At that time, the bar will be mov-
ing at a speed given by
VB = e inci = vssBI
VB
Vss = BI (1- 50)
The bar will continue to coast along at this no-load speed forever unless some ex-
ternal force disturbs it. When the motor is started, the velocity v, induced voltage
eind, current i, and induced force Find are as sketched in Figure 1-21.
To summarize, at starting, the linear dc machine behaves as follows:
1, Closing the switch produces a current flow i = VB / R.
2. The current flow produces a force on the bar given by F = ilB.