Page 109 - Electrical Equipment Handbook _ Troubleshooting and Maintenance
P. 109
AC MACHINE FUNDAMENTALS
5.10 CHAPTER FIVE
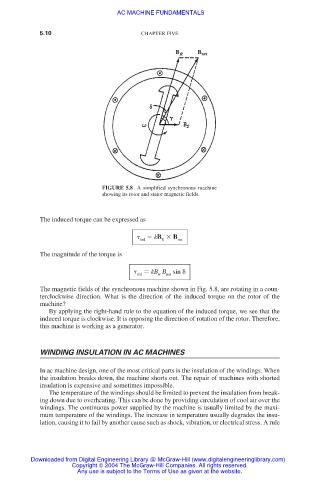
FIGURE 5.8 A simplified synchronous machine
showing its rotor and stator magnetic fields.
The induced torque can be expressed as
ind kB B net
R
The magnitude of the torque is
ind kB B sin
net
R
The magnetic fields of the synchronous machine shown in Fig. 5.8, are rotating in a coun-
terclockwise direction. What is the direction of the induced torque on the rotor of the
machine?
By applying the right-hand rule to the equation of the induced torque, we see that the
induced torque is clockwise. It is opposing the direction of rotation of the rotor. Therefore,
this machine is working as a generator.
WINDING INSULATION IN AC MACHINES
In ac machine design, one of the most critical parts is the insulation of the windings. When
the insulation breaks down, the machine shorts out. The repair of machines with shorted
insulation is expensive and sometimes impossible.
The temperature of the windings should be limited to prevent the insulation from break-
ing down due to overheating. This can be done by providing circulation of cool air over the
windings. The continuous power supplied by the machine is usually limited by the maxi-
mum temperature of the windings. The increase in temperature usually degrades the insu-
lation, causing it to fail by another cause such as shock, vibration, or electrical stress. A rule
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.