Page 108 - Electrical Equipment Handbook _ Troubleshooting and Maintenance
P. 108
AC MACHINE FUNDAMENTALS
AC MACHINE FUNDAMENTALS 5.9
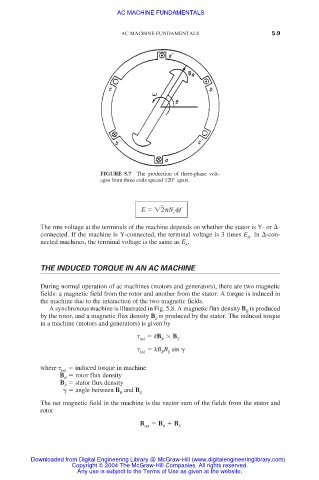
FIGURE 5.7 The production of three-phase volt-
ages from three coils spaced 120° apart.
E 2 N f
c
The rms voltage at the terminals of the machine depends on whether the stator is Y- or
-
connected. If the machine is Y-connected, the terminal voltage is 3 times E . In
-con-
A
nected machines, the terminal voltage is the same as E .
A
THE INDUCED TORQUE IN AN AC MACHINE
During normal operation of ac machines (motors and generators), there are two magnetic
fields: a magnetic field from the rotor and another from the stator. A torque is induced in
the machine due to the interaction of the two magnetic fields.
A synchronous machine is illustrated in Fig. 5.8. A magnetic flux density B is produced
R
by the rotor, and a magnetic flux density B is produced by the stator. The induced torque
S
in a machine (motors and generators) is given by
kB B
ind R S
kB B sin
ind R S
where induced torque in machine
ind
B rotor flux density
R
B stator flux density
S
angle between B and B
R S
The net magnetic field in the machine is the vector sum of the fields from the stator and
rotor
B B B
net R S
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.