Page 153 - Electrical Equipment Handbook _ Troubleshooting and Maintenance
P. 153
MAINTENANCE OF MOTORS
8.8 CHAPTER EIGHT
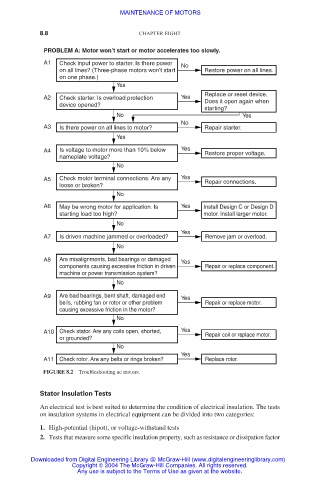
PROBLEM A: Motor won’t start or motor accelerates too slowly.
A1 Check input power to starter. Is there power
No
on all lines? (Three-phase motors won’t start Restore power on all lines.
on one phase.)
Yes
Replace or reset device.
A2 Check starter. Is overload protection Yes Does it open again when
device opened?
starting?
No Yes
No
A3 Is there power on all lines to motor? Repair starter.
Yes
A4 Is voltage to motor more than 10% below Yes Restore proper voltage.
nameplate voltage?
No
A5 Check motor terminal connections. Are any Yes Repair connections.
loose or broken?
No
A6 May be wrong motor for application. Is Yes Install Design C or Design D
starting load too high? motor. Install larger motor.
No
Yes
A7 Is driven machine jammed or overloaded? Remove jam or overload.
No
A8 Are misalignments, bad bearings or damaged Yes
components causing excessive friction in driven Repair or replace component.
machine or power transmission system?
No
A9 Are bad bearings, bent shaft, damaged end Yes
bells, rubbing fan or rotor or other problem Repair or replace motor.
causing excessive friction in the motor?
No
A10 Check stator. Are any coils open, shorted, Yes Repair coil or replace motor.
or grounded?
No
Yes
A11 Check rotor. Are any belts or rings broken? Replace rotor.
FIGURE 8.2 Troubleshooting ac motors.
Stator Insulation Tests
An electrical test is best suited to determine the condition of electrical insulation. The tests
on insulation systems in electrical equipment can be divided into two categories:
1. High-potential (hipot), or voltage-withstand tests
2. Tests that measure some specific insulation property, such as resistance or dissipation factor
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.