Page 79 - Electrical Installation in Hazardous Area
P. 79
Area classification for gases, vapours and mists 55
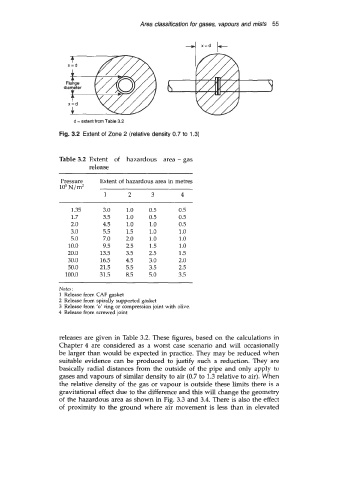
d = extent from Table 3.2
Fig. 3.2 Extent of Zone 2 (relative density 0.7 to 1.3)
Table 3.2 Extent of hazardous area - gas
release
Pressure Extent of hazardous area in metres
lo5 N/mZ
1 2 3 4
1.35 3.0 1.0 0.5 0.5
1.7 3.5 1.0 0.5 0.5
2.0 4.5 1.0 1 .o 0.5
3.0 5.5 1.5 1.0 1.0
5.0 7.0 2.0 1.0 1.0
10.0 9.5 2.5 1.5 1 .o
20.0 13.5 3.5 2.5 1.5
30.0 16.5 4.5 3.0 2.0
50.0 21.5 5.5 3.5 2.5
100.0 31.5 8.5 5.0 3.5
Notes:
1 Release from CAF gasket
2 Release from spirally supported gasket
3 Release from '0' ring or compression joint with olive.
4 Release from screwed joint
releases are given in Table 3.2. These figures, based on the calculations in
Chapter 4 are considered as a worst case scenario and will occasionally
be larger than would be expected in practice. They may be reduced when
suitable evidence can be produced to justify such a reduction. They are
basically radial distances from the outside of the pipe and only apply to
gases and vapours of similar density to air (0.7 to 1.3 relative to air). When
the relative density of the gas or vapour is outside these limits there is a
gravitational effect due to the difference and this will change the geometry
of the hazardous area as shown in Fig. 3.3 and 3.4. There is also the effect
of proximity to the ground where air movement is less than in elevated