Page 82 - Electrical Installation in Hazardous Area
P. 82
58 Electrical installations in hazardous areas
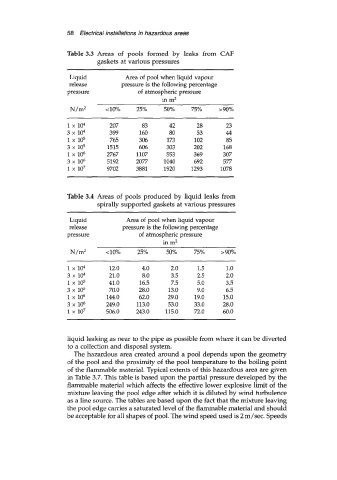
Table 3.3 Areas of pools formed by leaks from CAF
gaskets at various pressures
Liquid Area of pool when liquid vapour
release pressure is the following percentage
pressure of atmospheric pressure
in m2
N/mZ <lo% 25% 50% 75% >go%
1 x 104 207 83 42 28 23
3 x 104 399 160 80 53 44
1 x 105 765 306 173 102 85
3 x 105 1515 606 303 202 168
1 x 106 2767 1107 553 369 307
3 x 106 5192 2077 1040 692 577
1 x 107 9702 3881 1920 1293 1078
Table 3.4 Areas of pools produced by liquid leaks from
spirally supported gaskets at various pressures
Liquid Area of pool when liquid vapour
release pressure is the following percentage
pressure of atmospheric pressure
in m2
N/m2 <lo% 25% 50% 75% >go%
1 x 104 12.0 4.0 2.0 1.5 1.0
3x104 21.0 8.0 3.5 2.5 2.0
1 x 105 41 .O 16.5 7.5 5.0 3.5
3 x 105 70.0 28.0 13.0 9.0 6.5
1 x 106 144.0 62.0 29.0 19.0 15.0
3 x 106 249.0 113.0 53.0 33.0 28.0
1 x 107 506.0 243.0 115.0 72.0 60.0
liquid leaking as near to the pipe as possible from where it can be diverted
to a collection and disposal system.
The hazardous area created around a pool depends upon the geometry
of the pool and the proximity of the pool temperature to the boiling point
of the flammable material. Typical extents of this hazardous area are given
in Table 3.7. This table is based upon the partial pressure developed by the
flammable material which affects the effective lower explosive limit of the
mixture leaving the pool edge after which it is diluted by wind turbulence
as a line source. The tables are based upon the fact that the mixture leaving
the pool edge carries a saturated level of the flammable material and should
be acceptable for all shapes of pool. The wind speed used is 2 m/sec. Speeds