Page 195 - Electrical Safety of Low Voltage Systems
P. 195
178 Chapter Te n
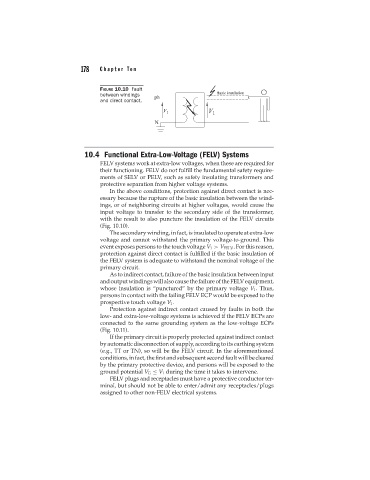
FIGURE 10.10 Fault
between windings
and direct contact.
10.4 Functional Extra-Low-Voltage (FELV) Systems
FELV systems work at extra-low voltages, when these are required for
their functioning. FELV do not fulfill the fundamental safety require-
ments of SELV or PELV, such as safety insulating transformers and
protective separation from higher voltage systems.
In the above conditions, protection against direct contact is nec-
essary because the rupture of the basic insulation between the wind-
ings, or of neighboring circuits at higher voltages, would cause the
input voltage to transfer to the secondary side of the transformer,
with the result to also puncture the insulation of the FELV circuits
(Fig. 10.10).
The secondary winding, in fact, is insulated to operate at extra-low
voltage and cannot withstand the primary voltage-to-ground. This
event exposes persons to the touch voltage V 1 > V FELV . For this reason,
protection against direct contact is fulfilled if the basic insulation of
the FELV system is adequate to withstand the nominal voltage of the
primary circuit.
As to indirect contact, failure of the basic insulation between input
andoutputwindingswillalsocausethefailureoftheFELVequipment,
whose insulation is “punctured” by the primary voltage V 1 . Thus,
persons in contact with the failing FELV ECP would be exposed to the
prospective touch voltage V 1 .
Protection against indirect contact caused by faults in both the
low- and extra-low-voltage systems is achieved if the FELV ECPs are
connected to the same grounding system as the low-voltage ECPs
(Fig. 10.11).
If the primary circuit is properly protected against indirect contact
by automatic disconnection of supply, according to its earthing system
(e.g., TT or TN), so will be the FELV circuit. In the aforementioned
conditions, in fact, the first and subsequent second fault will be cleared
by the primary protective device, and persons will be exposed to the
ground potential V G ≤ V 1 during the time it takes to intervene.
FELV plugs and receptacles must have a protective conductor ter-
minal, but should not be able to enter/admit any receptacles/plugs
assigned to other non-FELV electrical systems.