Page 190 - Electrical Safety of Low Voltage Systems
P. 190
Extra-Low-V oltage Systems 173
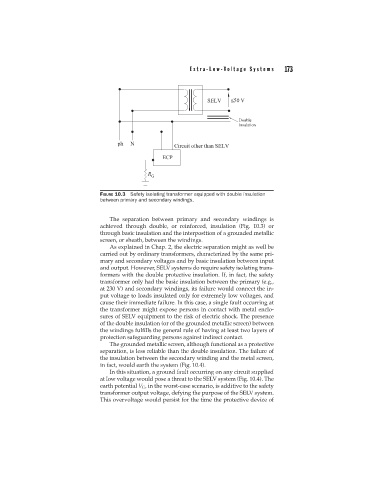
FIGURE 10.3 Safety isolating transformer equipped with double insulation
between primary and secondary windings.
The separation between primary and secondary windings is
achieved through double, or reinforced, insulation (Fig. 10.3) or
through basic insulation and the interposition of a grounded metallic
screen, or sheath, between the windings.
As explained in Chap. 2, the electric separation might as well be
carried out by ordinary transformers, characterized by the same pri-
mary and secondary voltages and by basic insulation between input
and output. However, SELV systems do require safety isolating trans-
formers with the double protective insulation. If, in fact, the safety
transformer only had the basic insulation between the primary (e.g.,
at 230 V) and secondary windings, its failure would connect the in-
put voltage to loads insulated only for extremely low voltages, and
cause their immediate failure. In this case, a single fault occurring at
the transformer might expose persons in contact with metal enclo-
sures of SELV equipment to the risk of electric shock. The presence
of the double insulation (or of the grounded metallic screen) between
the windings fulfills the general rule of having at least two layers of
protection safeguarding persons against indirect contact.
The grounded metallic screen, although functional as a protective
separation, is less reliable than the double insulation. The failure of
the insulation between the secondary winding and the metal screen,
in fact, would earth the system (Fig. 10.4).
In this situation, a ground fault occurring on any circuit supplied
at low voltage would pose a threat to the SELV system (Fig. 10.4). The
earth potential V G , in the worst-case scenario, is additive to the safety
transformer output voltage, defying the purpose of the SELV system.
This overvoltage would persist for the time the protective device of