Page 211 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 211
Chapter 10 Wire and Conductors 173
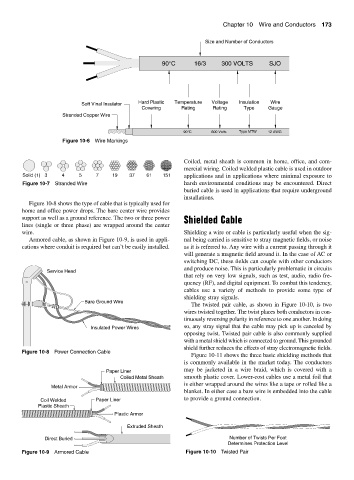
Size and Number of Conductors
90°C 16/3 300 VOLTS SJO
Soft Vinal Insulator Hard Plastic Temperature Voltage Insulation Wire
Covering Rating Rating Type Gauge
Stranded Copper Wire
90°C 600 Volts Type MTW 12 AWG
Figure 10-6 Wire Markings
Coiled, metal sheath is common in home, office, and com-
mercial wiring. Coiled welded plastic cable is used in outdoor
Solid (1) 3 4 5 7 19 37 61 151 applications and in applications where minimal exposure to
Figure 10-7 Stranded Wire harsh environmental conditions may be encountered. Direct
buried cable is used in applications that require underground
installations.
Figure 10-8 shows the type of cable that is typically used for
home and office power drops. The bare center wire provides
support as well as a ground reference. The two or three power Shielded Cable
lines (single or three phase) are wrapped around the center
wire. Shielding a wire or cable is particularly useful when the sig-
Armored cable, as shown in Figure 10-9, is used in appli- nal being carried is sensitive to stray magnetic fields, or noise
cations where conduit is required but can’t be easily installed. as it is referred to. Any wire with a current passing through it
will generate a magnetic field around it. In the case of AC or
switching DC, these fields can couple with other conductors
and produce noise. This is particularly problematic in circuits
Service Head
that rely on very low signals, such as test, audio, radio fre-
quency (RF), and digital equipment. To combat this tendency,
cables use a variety of methods to provide some type of
shielding stray signals.
Bare Ground Wire
The twisted pair cable, as shown in Figure 10-10, is two
wires twisted together. The twist places both conductors in con-
tinuously reversing polarity in reference to one another. In doing
Insulated Power Wires so, any stray signal that the cable may pick up is canceled by
opposing twist. Twisted pair cable is also commonly supplied
with a metal shield which is connected to ground. This grounded
shield further reduces the effects of stray electromagnetic fields.
Figure 10-8 Power Connection Cable
Figure 10-11 shows the three basic shielding methods that
is commonly available in the market today. The conductors
Paper Liner may be jacketed in a wire braid, which is covered with a
Coiled Metal Sheath smooth plastic cover. Lower-cost cables use a metal foil that
is either wrapped around the wires like a tape or rolled like a
Metal Armor
blanket. In either case a bare wire is embedded into the cable
Coil Welded Paper Liner to provide a ground connection.
Plastic Sheath
Plastic Armor
Extruded Sheath
Direct Buried Number of Twists Per Foot
Determines Protection Level
Figure 10-9 Armored Cable Figure 10-10 Twisted Pair