Page 294 - Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering 3rd Edition
P. 294
266 Collection and Analysis of Rate Data Chap. 5
alyst leaves the reactor in the product stream at the same rate at which it is fed,
to offset catalyst decay with time.
5.7.5 Straight-Through Transport Reactor
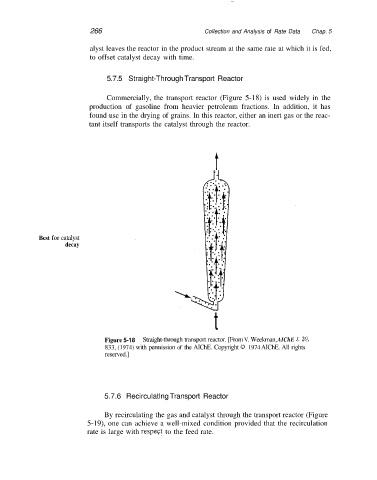
Commercially, the transport reactor (Figure 5-1 8) is used widely in the
production of gasoline from heavier petroleum fractions. In addition, it has
found use in the drying of grains. In this reactor, either an inert gas or the reac-
tant itself transports the catalyst through the reactor.
t
Best for catalyst
decay
t
Figure 5-18 Straight-through transport reactor. [From V. Weekman, AIChE J. 20,
833, (1974) with permission of the AIChE. Copyright 0 1974 AIChE. All rights
reserved.]
5.7.6 Recirculatlng Transport Reactor
By recirculating the gas and catalyst through the transport reactor (Figure
5-19), one can achieve a well-mixed condition provided that the recirculation
rate is large with respeGt to the feed rate.