Page 39 - Elements of Distribution Theory
P. 39
P1: JZP
052184472Xc01 CUNY148/Severini May 24, 2005 17:52
1.6 Density and Frequency Functions 25
F (x)
−
x
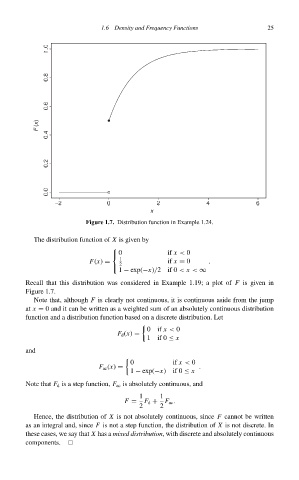
Figure 1.7. Distribution function in Example 1.24.
The distribution function of X is given by
0 if x < 0
1
F(x) = if x = 0 .
2
1 − exp(−x)/2if 0 < x < ∞
Recall that this distribution was considered in Example 1.19; a plot of F is given in
Figure 1.7.
Note that, although F is clearly not continuous, it is continuous aside from the jump
at x = 0 and it can be written as a weighted sum of an absolutely continuous distribution
function and a distribution function based on a discrete distribution. Let
0if x < 0
F d (x) =
1if 0 ≤ x
and
0 if x < 0
F ac (x) = .
1 − exp(−x)if 0 ≤ x
Note that F d is a step function, F ac is absolutely continuous, and
1 1
F = F d + F ac .
2 2
Hence, the distribution of X is not absolutely continuous, since F cannot be written
as an integral and, since F is not a step function, the distribution of X is not discrete. In
these cases, we say that X has a mixed distribution, with discrete and absolutely continuous
components.