Page 35 - Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering Ebook
P. 35
6 Mole Balances Chap. 1
( 1-2)
or
k,CA
The rate law is an -r, =
algebraic equation 1 + kzCA
For a given reaction, the particular concentration dependence that the rate law
2
follows (i.e., - rA = kC, or - rA = kCA or . . .) must be determined from exper-
imental observation. Equation (1-2) states that the rate of disappearance of A is
equal to a rate constant k times the square of the concentration of A. By conven-
tion, r, is the rate of formation of A; consequently, -rA is the rate of disappear-
ance of A. Throughout this book the phrase rate of generation means exactly the
same as the phrase rate offormation, and these phrases are used interchangeably.
1.2 The General Mole Balance Equation
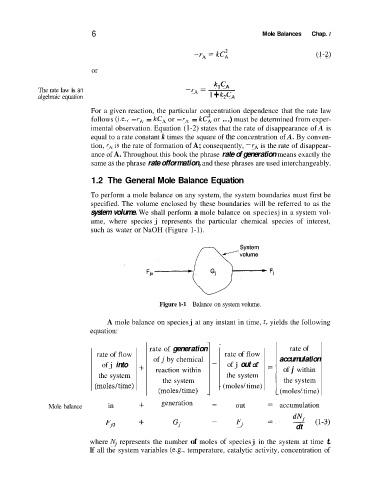
To perform a mole balance on any system, the system boundaries must first be
specified. The volume enclosed by these boundaries will be referred to as the
system volume. We shall perform a mole balance on speciesj in a system vol-
ume, where species j represents the particular chemical species of interest,
such as water or NaOH (Figure 1-1).
Figure 1-1 Balance on system volume.
A mole balance on species j at any instant in time, t, yields the following
equation:
-
rate of generation - rate of
rate of flow of j by chemical rate of flow accumulation
of j into - of j out of
reaction within of j within
the system the system
the system the system
(moles/time) - (moles / time)
(moles/time) - (moles / time)
Mole balance in generation - out accumulation
-
- dNj
Fjo Gi Fj dt (1-3)
where Nj represents the number of moles of species j in the system at time t.
If all the system variables (e.g., temperature, catalytic activity, concentration of