Page 119 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioTechnology
P. 119
P1: GLQ/GUB P2: FYK Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN007K-319 July 2, 2001 17:53
Hybridomas, Genetic Engineering of 429
specific molecule (called the antigen) with high affinity.
The other important functional component of the molecule
is the effector site which is found in the constant region.
The effector functions can be mediated by binding com-
plement (C1q) and those mediated by binding to Fc re-
ceptors of specific cells. Complement activation leads to
the activation of leukocytes and phagocytosis. The Fc re-
ceptors are on certain cells of the immune system such
as phagocytes and natural killer (NK) cells. Binding to
receptors in these cells produces a variety of biological
responses including antibody-dependent cellular cytotox-
icity (ADCC), phagocytosis, endocytosis, and release of
inflammatory agents.
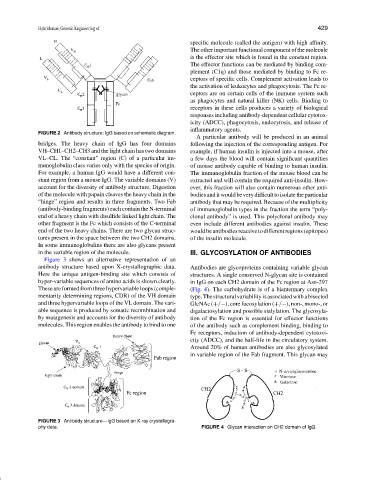
FIGURE 2 Antibody structure: IgG based on schematic diagram.
A particular antibody will be produced in an animal
bridges. The heavy chain of IgG has four domains following the injection of the corresponding antigen. For
VH–CH1–CH2–CH3 and the light chain has two domains example, if human insulin is injected into a mouse, after
VL–CL. The “constant” region (C) of a particular im- a few days the blood will contain significant quantities
munoglobulin class varies only with the species of origin. of mouse antibody capable of binding to human insulin.
For example, a human IgG would have a different con- The immunoglobulin fraction of the mouse blood can be
stant region from a mouse IgG. The variable domains (V) extracted and will contain the required anti-insulin. How-
account for the diversity of antibody structure. Digestion ever, this fraction will also contain numerous other anti-
of the molecule with papain cleaves the heavy chain in the bodiesanditwouldbeverydifficulttoisolatetheparticular
“hinge” region and results in three fragments. Two Fab antibody that may be required. Because of the multiplicity
(antibody-binding fragments) each contain the N-terminal of immunoglobulin types in the fraction the term “poly-
end of a heavy chain with disulfide linked light chain. The clonal antibody” is used. This polyclonal antibody may
other fragment is the Fc which consists of the C-terminal even include different antibodies against insulin. These
end of the two heavy chains. There are two glycan struc- wouldbeantibodiesreactivetodifferentregions(epitopes)
tures present in the space between the two CH2 domains. of the insulin molecule.
In some immunoglobulins there are also glycans present
in the variable region of the molecule. III. GLYCOSYLATION OF ANTIBODIES
Figure 3 shows an alternative representation of an
antibody structure based upon X-crystallographic data. Antibodies are glycoproteins containing variable glycan
Here the unique antigen-binding site which consists of structures. A single conserved N-glycan site is contained
hyper-variable sequences of amino acids is shown clearly. in IgG on each CH2 domain of the Fc region at Asn-297
These are formed from three hypervariable loops (comple- (Fig. 4). The carbohydrate is of a biantennary complex
mentarity determining regions, CDR) of the VH domain type.Thestructuralvariabilityisassociatedwithabisected
and three hypervariable loops of the VL domain. The vari- GlcNAc (+/−), core fucosylation (+/−), non-, mono-, or
able sequence is produced by somatic recombination and digalactosylation and possible sialylation. The glycosyla-
by mutagenesis and accounts for the diversity of antibody tion of the Fc region is essential for effector functions
molecules. This region enables the antibody to bind to one of the antibody such as complement binding, binding to
Fc receptors, induction of antibody-dependent cytotoxi-
city (ADCC), and the half-life in the circulatory system.
Around 20% of human antibodies are also glycosylated
in variable region of the Fab fragment. This glycan may
FIGURE 3 Antibody structure—IgG based on X-ray crystallogra-
phy data. FIGURE 4 Glycan interaction on CH2 domain of IgG.