Page 274 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioTechnology
P. 274
P1: GPB/GRB P2: GLQ Final pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN016J-783 August 1, 2001 10:58
Tissue Engineering 825
TABLE V Growth Factors Commonly Used in Tissue
Engineering
Growth factor Target cell
Epidermal growth factor Keratinocytes, hepatocytes
Hepatocyte growth factor, Epithelial cells
scatter factor
Interleukin-2 White blood cells
Platelet-derived growth factor Fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells
(PDGF)
Fibroblast growth factor Fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells,
endothelial cells
Vascular endothelial growth Endothelial cells
factor (VEGF)
Nerve growth factor Neurons
Insulin-like growth factor Muscle, keratinocytes
Osteogenic protein 1 Osteoblasts
of the host’s surrounding cells to regenerate the damaged
or missing tissue. Control of the function and growth of the
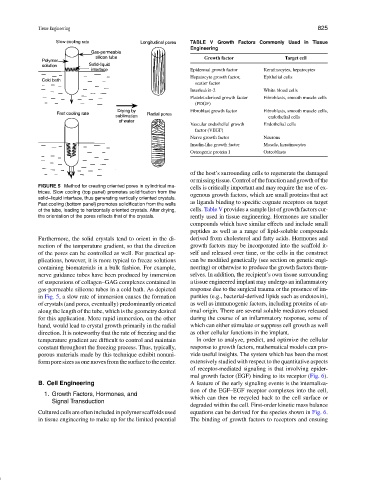
FIGURE 5 Method for creating oriented pores in cylindrical ma-
cells is critically important and may require the use of ex-
trices. Slow cooling (top panel) promotes solidification from the
ogenous growth factors, which are small proteins that act
solid–liquid interface, thus generating vertically oriented crystals.
as ligands binding to specific cognate receptors on target
Fast cooling (bottom panel) promotes solidification from the walls
of the tube, leading to horizontally oriented crystals. After drying, cells. Table V provides a sample list of growth factors cur-
the orientation of the pores reflects that of the crystals. rently used in tissue engineering. Hormones are smaller
compounds which have similar effects and include small
peptides as well as a range of lipid-soluble compounds
Furthermore, the solid crystals tend to orient in the di- derived from cholesterol and fatty acids. Hormones and
rection of the temperature gradient, so that the direction growth factors may be incorporated into the scaffold it-
of the pores can be controlled as well. For practical ap- self and released over time, or the cells in the construct
plications, however, it is more typical to freeze solutions can be modified genetically (see section on genetic engi-
containing biomaterials in a bulk fashion. For example, neering) or otherwise to produce the growth factors them-
nerve guidance tubes have been produced by immersion selves. In addition, the recipient’s own tissue surrounding
of suspensions of collagen–GAG complexes contained in a tissue engineered implant may undergo an inflammatory
gas-permeable silicone tubes in a cold bath. As depicted response due to the surgical trauma or the presence of im-
in Fig. 5, a slow rate of immersion causes the formation purities (e.g., bacterial-derived lipids such as endotoxin),
of crystals (and pores, eventually) predominantly oriented as well as immunogenic factors, including proteins of an-
along the length of the tube, which is the geometry desired imal origin. There are several soluble mediators released
for this application. More rapid immersion, on the other during the course of an inflammatory response, some of
hand, would lead to crystal growth primarily in the radial which can either stimulate or suppress cell growth as well
direction. It is noteworthy that the rate of freezing and the as other cellular functions in the implant.
temperature gradient are difficult to control and maintain In order to analyze, predict, and optimize the cellular
constant throughout the freezing process. Thus, typically, response to growth factors, mathematical models can pro-
porous materials made by this technique exhibit nonuni- vide useful insights. The system which has been the most
formporesizesasonemovesfromthesurfacetothecenter. extensively studied with respect to the quantitative aspects
of receptor-mediated signaling is that involving epider-
mal growth factor (EGF) binding to its receptor (Fig. 6).
B. Cell Engineering A feature of the early signaling events is the internaliza-
tion of the EGF–EGF receptor complexes into the cell,
1. Growth Factors, Hormones, and
which can then be recycled back to the cell surface or
Signal Transduction
degraded within the cell. First-order kinetic mass balance
Cultured cells are often included in polymer scaffolds used equations can be derived for the species shown in Fig. 6.
in tissue engineering to make up for the limited potential The binding of growth factors to receptors and ensuing