Page 276 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioTechnology
P. 276
P1: GPB/GRB P2: GLQ Final pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN016J-783 August 1, 2001 10:58
Tissue Engineering 827
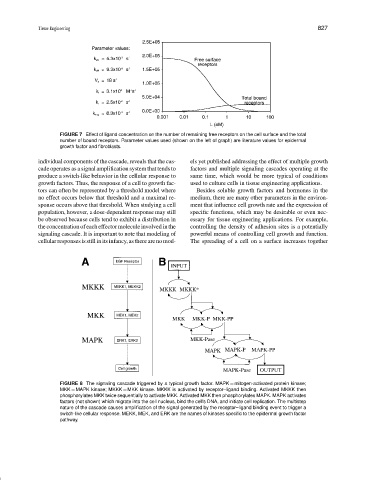
FIGURE 7 Effect of ligand concentration on the number of remaining free receptors on the cell surface and the total
number of bound receptors. Parameter values used (shown on the left of graph) are literature values for epidermal
growth factor and fibroblasts.
individual components of the cascade, reveals that the cas- els yet published addressing the effect of multiple growth
cade operates as a signal amplification system that tends to factors and multiple signaling cascades operating at the
produce a switch-like behavior in the cellular response to same time, which would be more typical of conditions
growth factors. Thus, the response of a cell to growth fac- used to culture cells in tissue engineering applications.
tors can often be represented by a threshold model where Besides soluble growth factors and hormones in the
no effect occurs below that threshold and a maximal re- medium, there are many other parameters in the environ-
sponse occurs above that threshold. When studying a cell ment that influence cell growth rate and the expression of
population, however, a dose-dependent response may still specific functions, which may be desirable or even nec-
be observed because cells tend to exhibit a distribution in essary for tissue engineering applications. For example,
the concentration of each effector molecule involved in the controlling the density of adhesion sites is a potentially
signaling cascade. It is important to note that modeling of powerful means of controlling cell growth and function.
cellular responses is still in its infancy, as there are no mod- The spreading of a cell on a surface increases together
FIGURE 8 The signaling cascade triggered by a typical growth factor. MAPK = mitogen-activated protein kinase;
MKK = MAPK kinase; MKKK = MKK kinase. MKKK is activated by receptor–ligand binding. Activated MKKK then
phosphorylates MKK twice sequentially to activate MKK. Activated MKK then phosphorylates MAPK. MAPK activates
factors (not shown) which migrate into the cell nucleus, bind the cell’s DNA, and initiate cell replication. The multistep
nature of the cascade causes amplification of the signal generated by the receptor–ligand binding event to trigger a
switch-like cellular response. MEKK, MEK, and ERK are the names of kinases specific to the epidermal growth factor
pathway.