Page 109 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Chemical Engineering
P. 109
P1: ZBU 2nd Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002G-87 May 19, 2001 20:3
Catalyst Characterization 507
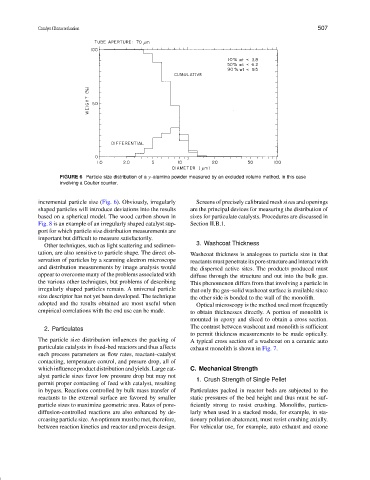
FIGURE 6 Particle size distribution of a γ -alumina powder measured by an excluded volume method, in this case
involving a Coulter counter.
incremental particle size (Fig. 6). Obviously, irregularly Screens of precisely calibrated mesh sizes and openings
shaped particles will introduce deviations into the results are the principal devices for measuring the distribution of
based on a spherical model. The wood carbon shown in sizes for particulate catalysts. Procedures are discussed in
Fig. 8 is an example of an irregularly shaped catalyst sup- Section II.B.1.
port for which particle size distribution measurements are
important but difficult to measure satisfactorily.
Other techniques, such as light scattering and sedimen- 3. Washcoat Thickness
tation, are also sensitive to particle shape. The direct ob- Washcoat thickness is analogous to particle size in that
servation of particles by a scanning electron microscope reactantsmustpenetrateitsporestructureandinteractwith
and distribution measurements by image analysis would the dispersed active sites. The products produced must
appear to overcome many of the problems associated with diffuse through the structure and out into the bulk gas.
the various other techniques, but problems of describing This phenomenon differs from that involving a particle in
irregularly shaped particles remain. A universal particle that only the gas–solid washcoat surface is available since
size descriptor has not yet been developed. The technique the other side is bonded to the wall of the monolith.
adopted and the results obtained are most useful when Optical microscopy is the method used most frequently
empirical correlations with the end use can be made. to obtain thicknesses directly. A portion of monolith is
mounted in epoxy and sliced to obtain a cross section.
The contrast between washcoat and monolith is sufficient
2. Particulates
to permit thickness measurements to be made optically.
The particle size distribution influences the packing of A typical cross section of a washcoat on a ceramic auto
particulate catalysts in fixed-bed reactors and thus affects exhaust monolith is shown in Fig. 7.
such process parameters as flow rates, reactant–catalyst
contacting, temperature control, and presure drop, all of
which influence product distribution and yields. Large cat- C. Mechanical Strength
alyst particle sizes favor low pressure drop but may not
1. Crush Strength of Single Pellet
permit proper contacting of feed with catalyst, resulting
in bypass. Reactions controlled by bulk mass transfer of Particulates packed in reactor beds are subjected to the
reactants to the external surface are favored by smaller static pressures of the bed height and thus must be suf-
particle sizes to maximize geometric area. Rates of pore- ficiently strong to resist crushing. Monoliths, particu-
diffusion-controlled reactions are also enhanced by de- larly when used in a stacked mode, for example, in sta-
creasing particle size. An optimum must be met, therefore, tionary pollution abatement, must resist crushing axially.
between reaction kinetics and reactor and process design. For vehicular use, for example, auto exhaust and ozone