Page 112 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Chemical Engineering
P. 112
P1: ZBU 2nd Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002G-87 May 19, 2001 20:3
510 Catalyst Characterization
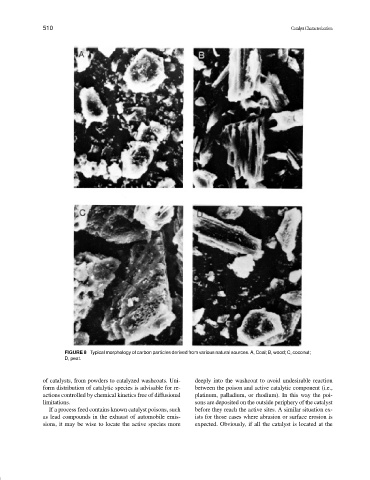
FIGURE 8 Typical morphology of carbon particles derived from various natural sources. A, Coal; B, wood; C, coconut;
D, peat.
of catalysts, from powders to catalyzed washcoats. Uni- deeply into the washcoat to avoid undesirable reaction
form distribution of catalytic species is advisable for re- between the poison and active catalytic component (i.e.,
actions controlled by chemical kinetics free of diffusional platinum, palladium, or rhodium). In this way the poi-
limitations. sons are deposited on the outside periphery of the catalyst
If a process feed contains known catalyst poisons, such before they reach the active sites. A similar situation ex-
as lead compounds in the exhaust of automobile emis- ists for those cases where abrasion or surface erosion is
sions, it may be wise to locate the active species more expected. Obviously, if all the catalyst is located at the