Page 148 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 148
P1: GTY/GWT P2: GLM Final
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN006K-933 June 29, 2001 12:14
258 Fuel Chemistry
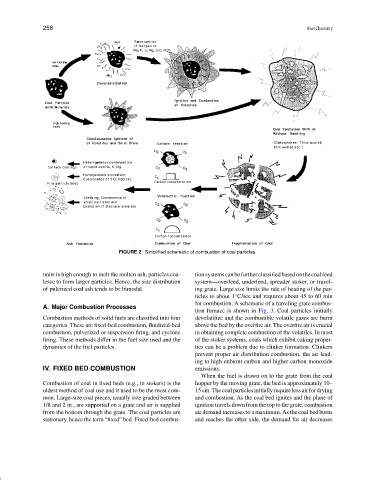
FIGURE 2 Simplified schematic of combustion of coal particles.
units is high enough to melt the molten ash, particles coa- tionsystemscanbefurtherclassifiedbasedonthecoalfeed
lesce to form larger particles. Hence, the size distribution system—overfeed, underfeed, spreader stoker, or travel-
of pulerized coal ash tends to be bimodal. ing grate. Large size limits the rate of heating of the par-
ticles to about 1 C/sec and requires about 45 to 60 min
◦
for combustion. A schematic of a traveling grate combus-
A. Major Combustion Processes
tion furnace is shown in Fig. 3. Coal particles initially
Combustion methods of solid fuels are classified into four devolatilize and the combustible volatile gases are burnt
categories. These are fixed-bed combustion, fluidized-bed above the bed by the overfire air. The overfire air is crucial
combustion, pulverized or suspension firing, and cyclone in obtaining complete combustion of the volatiles. In most
firing. These methods differ in the fuel size used and the of the stoker systems, coals which exhibit caking proper-
dynamics of the fuel particles. ties can be a problem due to clinker formation. Clinkers
prevent proper air distribution combustion, the air lead-
ing to high unburnt carbon and higher carbon monoxide
IV. FIXED BED COMBUSTION emissions.
When the fuel is drawn on to the grate from the coal
Combustion of coal in fixed beds (e.g., in stokers) is the hopper by the moving grate, the bed is approximately 10–
oldest method of coal use and it used to be the most com- 15cm.Thecoalparticlesinitiallyrequirelessairfordrying
mon. Large-size coal pieces, usually size graded between and combustion. As the coal bed ignites and the plane of
1/8 and 2 in., are supported on a grate and air is supplied ignition travels down from the top to the grate, combustion
from the bottom through the grate. The coal particles are air demand increases to a maximum. As the coal bed burns
stationary, hence the term “fixed” bed. Fixed-bed combus- and reaches the other side, the demand for air decreases