Page 90 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 90
P1: LLL/LLL P2: FJU Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002C-80 May 25, 2001 20:18
398 Carbohydrates
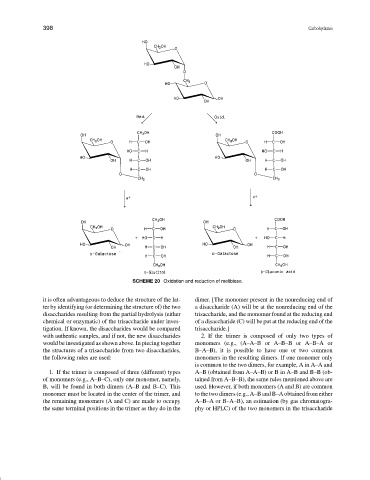
SCHEME 20 Oxidation and reduction of melibiose.
it is often advantageous to deduce the structure of the lat- dimer. [The monomer present in the nonreducing end of
ter by identifying (or determining the structure of) the two a disaccharide (A) will be at the nonreducing end of the
disaccharides resulting from the partial hydrolysis (either trisaccharide, and the monomer found at the reducing end
chemical or enzymatic) of the trisaccharide under inves- of a disaccharide (C) will be put at the reducing end of the
tigation. If known, the disaccharides would be compared trisaccharide.]
with authentic samples, and if not, the new disaccharides 2. If the trimer is composed of only two types of
would be investigated as shown above. In piecing together monomers (e.g., (A–A–BorA–B–BorA–B–Aor
the structures of a trisaccharide from two disaccharides, B–A–B), it is possible to have one or two common
the following rules are used: monomers in the resulting dimers. If one monomer only
is common to the two dimers, for example, A in A–A and
1. If the trimer is composed of three (different) types A–B (obtained from A–A–B) orBinA–B and B–B (ob-
of monomers (e.g., A–B–C), only one monomer, namely, tained from A–B–B), the same rules mentioned above are
B, will be found in both dimers (A–B and B–C). This used. However, if both monomers (A and B) are common
monomer must be located in the center of the trimer, and to the two dimers (e.g., A–B and B–A obtained from either
the remaining monomers (A and C) are made to occupy A–B–AorB–A–B), an estimation (by gas chromatogra-
the same terminal positions in the trimer as they do in the phy or HPLC) of the two monomers in the trisaccharide