Page 141 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 141
P1: GLM/GJK P2: GRB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology En005H-218 June 15, 2001 20:33
Electrophoresis 369
egg protein ovalbumin has an isoelectric point of pH 4.5,
but at pH 7 the number of charges determined from pH
titration was about −17, while that from the mobilities was
−10; the difference is thought to be caused by preferential
−
adsorption of Cl .
One major contribution made by electrophoretic ex-
periments with proteins was the measurement of inter-
actions between peptide chains of complex proteins (such
as hemoglobin) with other ions, as well as their own self-
association. Most biologically active proteins are formed
from aggregates of peptide chains (the subunits), and these
chains combine through a variety of weak intermolecular
forces such as salt links or van der Waals dispersion forces.
If the energies of these intermolecular forces fall within
a range similar to that arising from thermal activities, the
aggregates dissociate on dilution to produce an equilib-
rium mixture containing free subunits plus the aggregate.
Electrophoresis provided one of the two experimental pro-
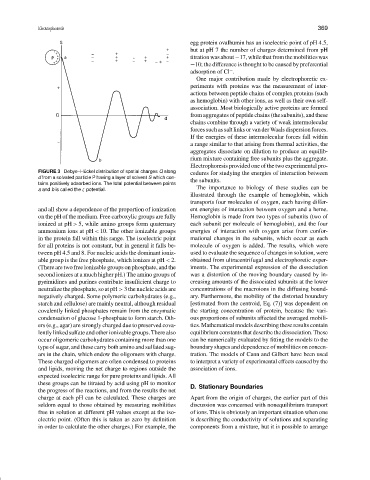
FIGURE 3 Debye–H¨uckel distribution of spatial charges Q along
cedures for studying the energies of interaction between
d from a solvated particle P having a layer of solvent S which con-
the subunits.
tains positively adsorbed ions. The total potential between points
The importance to biology of these studies can be
a and b is called the ζ potential.
illustrated through the example of hemoglobin, which
transports four molecules of oxygen, each having differ-
and all show a dependence of the proportion of ionization ent energies of interaction between oxygen and a heme.
on the pH of the medium. Free carboxylic groups are fully Hemoglobin is made from two types of subunits (two of
ionized at pH > 5, while amino groups form quaternary each subunit per molecule of hemoglobin), and the four
ammonium ions at pH < 10. The other ionizable groups energies of interaction with oxygen arise from confor-
in the protein fall within this range. The isoelectric point mational changes in the subunits, which occur as each
for all proteins is not constant, but in general it falls be- molecule of oxygen is added. The results, which were
tween pH 4.5 and 8. For nucleic acids the dominant ioniz- used to evaluate the sequence of changes in solution, were
able group is the free phosphate, which ionizes at pH < 2. obtained from ultracentrifugal and electrophoretic exper-
(There are two free ionizable groups on phosphate, and the iments. The experimental expression of the dissociation
second ionizes at a much higher pH.) The amino groups of was a distortion of the moving boundary caused by in-
pyrimidines and purines contribute insufficient charge to creasing amounts of the dissociated subunits at the lower
neutralize the phosphate, so at pH > 3 the nucleic acids are concentrations of the macroions in the diffusing bound-
negatively charged. Some polymeric carbohydrates (e.g., ary. Furthermore, the mobility of the distorted boundary
starch and cellulose) are mainly neutral, although residual [estimated from the centroid, Eq. (7)] was dependent on
covalently linked phosphates remain from the enzymatic the starting concentration of protein, because the vari-
condensation of glucose 1-phosphate to form starch. Oth- ous proportions of subunits affected the averaged mobili-
ers (e.g., agar) are strongly charged due to preserved cova- ties. Mathematical models describing these results contain
lently linked sulfate and other ionizable groups. There also equilibrium constants that describe the dissociation. These
occur oligomeric carbohydrates containing more than one can be numerically evaluated by fitting the models to the
type of sugar, and these carry both amino and sulfated sug- boundary shapes and dependence of mobilities on concen-
ars in the chain, which endow the oligomers with charge. tration. The models of Cann and Gilbert have been used
These charged oligomers are often condensed to proteins to interpret a variety of experimental effects caused by the
and lipids, moving the net charge to regions outside the association of ions.
expected isoelectric range for pure proteins and lipids. All
these groups can be titrated by acid using pH to monitor
D. Stationary Boundaries
the progress of the reactions, and from the results the net
charge at each pH can be calculated. These charges are Apart from the origin of charges, the earlier part of this
seldom equal to those obtained by measuring mobilities discussion was concerned with nonequilibrium transport
free in solution at different pH values except at the iso- of ions. This is obviously an important situation when one
electric point. (Often this is taken as zero by definition is describing the conductivity of solutions and separating
in order to calculate the other charges.) For example, the components from a mixture, but it is possible to arrange