Page 43 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 43
P1: FYK/LSX Revised Pages P2: FWQ/FPW QC: FYD
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology en001d42 April 28, 2001 15:9
Atomic Spectrometry 767
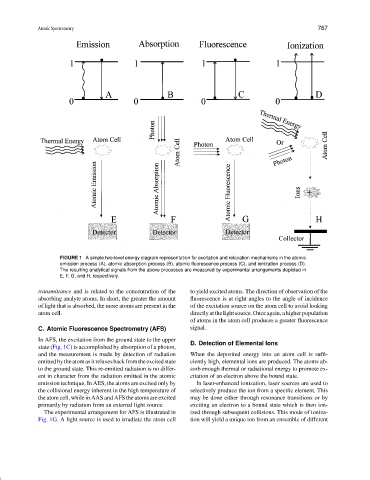
FIGURE 1 A simple two-level energy diagram representation for excitation and relaxation mechanisms in the atomic
emission process (A), atomic absorption process (B), atomic fluorescence process (C), and ionization process (D).
The resulting analytical signals from the above processes are measured by experimental arrangements depicted in
E, F, G, and H, respectively.
transmittance and is related to the concentration of the to yield excited atoms. The direction of observation of the
absorbing analyte atoms. In short, the greater the amount fluorescence is at right angles to the angle of incidence
of light that is absorbed, the more atoms are present in the of the excitation source on the atom cell to avoid looking
atom cell. directlyatthelightsource.Onceagain,ahigherpopulation
of atoms in the atom cell produces a greater fluorescence
C. Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry (AFS) signal.
In AFS, the excitation from the ground state to the upper D. Detection of Elemental Ions
state (Fig. 1C) is accomplished by absorption of a photon,
and the measurement is made by detection of radiation When the deposited energy into an atom cell is suffi-
emittedbytheatomasitrelaxesbackfromtheexcitedstate ciently high, elemental ions are produced. The atoms ab-
to the ground state. This re-emitted radiation is no differ- sorb enough thermal or radiational energy to promote ex-
ent in character from the radiation emitted in the atomic citation of an electron above the bound state.
emission technique. In AES, the atoms are excited only by In laser-enhanced ionization, laser sources are used to
the collisional energy inherent in the high temperature of selectively produce the ion from a specific element. This
the atom cell, while in AAS and AFS the atoms are excited may be done either through resonance transitions or by
primarily by radiation from an external light source. exciting an electron to a bound state which is then ion-
The experimental arrangement for AFS is illustrated in ized through subsequent collisions. This mode of ioniza-
Fig. 1G. A light source is used to irradiate the atom cell tion will yield a unique ion from an ensemble of different