Page 77 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 77
P1: LDK Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002E-79 May 17, 2001 20:28
Capillary Zone Electrophoresis 363
Mobility and selectivity in CZE are most profoundly af- ity monitoring of protein therapeutics; clinical analysis of
fected by analyte charge, and selection of the electrolyte serum proteins; and quality control of wines. The CZE
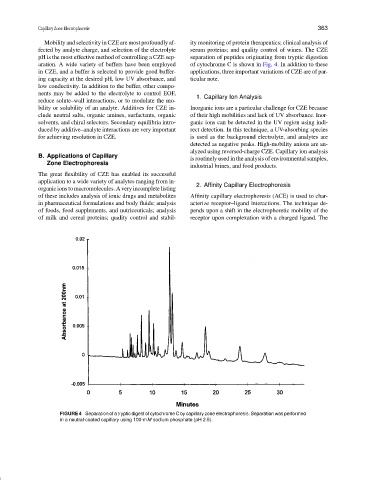
pH is the most effective method of controlling a CZE sep- separation of peptides originating from tryptic digestion
aration. A wide variety of buffers have been employed of cytochrome C is shown in Fig. 4. In addition to these
in CZE, and a buffer is selected to provide good buffer- applications, three important variations of CZE are of par-
ing capacity at the desired pH, low UV absorbance, and ticular note.
low conductivity. In addition to the buffer, other compo-
nents may be added to the electrolyte to control EOF,
1. Capillary Ion Analysis
reduce solute–wall interactions, or to modulate the mo-
bility or solubility of an analyte. Additives for CZE in- Inorganic ions are a particular challenge for CZE because
clude neutral salts, organic amines, surfactants, organic of their high mobilities and lack of UV absorbance. Inor-
solvents, and chiral selectors. Secondary equilibria intro- ganic ions can be detected in the UV region using indi-
duced by additive–analyte interactions are very important rect detection. In this technique, a UV-absorbing species
for achieving resolution in CZE. is used as the background electrolyte, and analytes are
detected as negative peaks. High-mobility anions are an-
alyzed using reversed-charge CZE. Capillary ion analysis
B. Applications of Capillary
is routinely used in the analysis of environmental samples,
Zone Electrophoresis
industrial brines, and food products.
The great flexibility of CZE has enabled its successful
application to a wide variety of analytes ranging from in- 2. Affinity Capillary Electrophoresis
organic ions to macromolecules. A very incomplete listing
of these includes analysis of ionic drugs and metabolites Affinity capillary electrophoresis (ACE) is used to char-
in pharmaceutical formulations and body fluids; analysis acterize receptor–ligand interactions. The technique de-
of foods, food supplements, and nutriceuticals; analysis pends upon a shift in the electrophoretic mobility of the
of milk and cereal proteins; quality control and stabil- receptor upon complexation with a charged ligand. The
FIGURE 4 Separation of a tryptic digest of cytochrome C by capillary zone electrophoresis. Separation was performed
in a neutral-coated capillary using 100-mM sodium phosphate (pH 2.5).