Page 79 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 79
P1: LDK Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002E-79 May 17, 2001 20:28
Capillary Zone Electrophoresis 365
reproducible migration patterns can be difficult, particu- pholyte blends are used which generate gradients of over
larly when using electroosmotic mobilization. 8 pH units (e.g., pH 3–10); for high-resolution separation
In two-step CIEF, focusing and mobilization are per- of a few proteins, narrow-range ampholyte blends are used
formed separately. Initially, the entire capillary is filled to generate gradients of 1 to 2 pH units.
with a mixture of sample and ampholytes, high voltage
is applied, and the focusing progress is monitored by the B. Applications of Capillary
decrease in operating current. Once equilibrium has been Isoelectric Focusing
established,themobilizationstepisbegun.Themobilizing
The high resolving power of CIEF enables separation of
forcemaybepressure,vacuum,gravity,orelectrophoretic.
protein species with small differences in isoelectric points.
In all cases, the electric field is maintained to prevent defo-
Capillary IEF has been applied to the analysis of protein
cusing of zones during mobilization. Electrophoretic mo-
glycoforms, protein clips, and deamidation products. The
bilization is accomplished by changing the composition of
technique has also been used for analysis of hemoglobin
the anolyte or catholyte, usually by the addition of a salt,
variants and glycated hemoglobins. It provides a rapid and
buffer, or zwitterion solution. This change in composi-
convenient method for estimating the isoelectric point of
tion produces a progressive shift in pH down the capillary,
an unknown protein. On-line CIEF–MS is being inves-
causing electrophoretic migration of focused proteins past
tigated as an instrumental counterpart to analytical two-
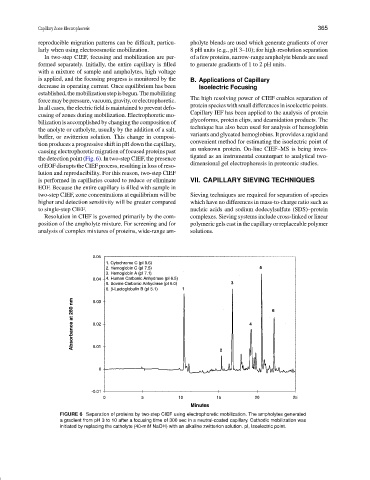
the detection point (Fig. 6). In two-step CIEF, the presence
dimensional gel electrophoresis in proteomic studies.
of EOF disrupts the CIEF process, resulting in loss of reso-
lution and reproducibility. For this reason, two-step CIEF
is performed in capillaries coated to reduce or eliminate VII. CAPILLARY SIEVING TECHNIQUES
EOF. Because the entire capillary is filled with sample in
two-step CIEF, zone concentrations at equilibrium will be Sieving techniques are required for separation of species
higher and detection sensitivity will be greater compared which have no differences in mass-to-charge ratio such as
to single-step CIEF. nucleic acids and sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS)–protein
Resolution in CIEF is governed primarily by the com- complexes. Sieving systems include cross-linked or linear
position of the ampholyte mixture. For screening and for polymeric gels cast in the capillary or replaceable polymer
analysis of complex mixtures of proteins, wide-range am- solutions.
FIGURE 6 Separation of proteins by two-step CIEF using electrophoretic mobilization. The ampholytes generated
a gradient from pH 3 to 10 after a focusing time of 300 sec in a neutral-coated capillary. Cathodic mobilization was
initiated by replacing the catholyte (40-mM NaOH) with an alkaline zwitterion solution. pI, Isoelectric point.