Page 81 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 81
P1: LDK Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002E-79 May 17, 2001 20:28
Capillary Zone Electrophoresis 367
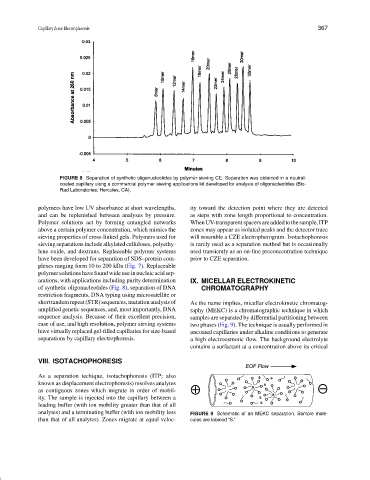
FIGURE 8 Separation of synthetic oligonucleotides by polymer-sieving CE. Separation was obtained in a neutral-
coated capillary uisng a commercial polymer-sieving applications kit developed for analysis of oligonucleotides (Bio-
Rad Laboratories; Hercules, CA).
polymers have low UV absorbance at short wavelengths, ity toward the detection point where they are detected
and can be replenished between analyses by pressure. as steps with zone length proportional to concentration.
Polymer solutions act by forming entangled networks WhenUV-transparentspacersareaddedtothesample,ITP
above a certain polymer concentration, which mimics the zones may appear as isolated peaks and the detector trace
sieving properties of cross-linked gels. Polymers used for will resemble a CZE electropherogram. Isotachophoresis
sieving separations include alkylated celluloses, polyethy- is rarely used as a separation method but is occasionally
lene oxide, and dextrans. Replaceable polymer systems used transiently as an on-line preconcentration technique
have been developed for separation of SDS–protein com- prior to CZE separation.
plexes ranging form 10 to 200 kDa (Fig. 7). Replaceable
polymer solutions have found wide use in nucleic acid sep-
arations, with applications including purity determination IX. MICELLAR ELECTROKINETIC
of synthetic oligonucleotides (Fig. 8), separation of DNA CHROMATOGRAPHY
restriction fragments, DNA typing using microsatellite or
shorttandemrepeat(STR)sequences,mutationanalysisof As the name implies, micellar electrokinetic chromatog-
amplified genetic sequences, and, most importantly, DNA raphy (MEKC) is a chromatographic technique in which
sequence analysis. Because of their excellent precision, samples are separated by differential partitioning between
ease of use, and high resolution, polymer sieving systems two phases (Fig. 9). The technique is usually performed in
have virtually replaced gel-filled capillaries for size-based uncoated capillaries under alkaline conditions to generate
separations by capillary electrophoresis. a high electroosmotic flow. The background electrolyte
contains a surfactant at a concentration above its critical
VIII. ISOTACHOPHORESIS
As a separation techique, isotachophoresis (ITP; also
known as displacement electrophoresis) resolves analytes
as contiguous zones which migrate in order of mobil-
ity. The sample is injected into the capillary between a
leading buffer (with ion mobility greater than that of all
analytes) and a terminating buffer (with ion mobility less FIGURE 9 Schematic of an MEKC separation. Sample mole-
than that of all analytes). Zones migrate at equal veloc- cules are labeled “S.”