Page 78 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 78
P1: LDK Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002E-79 May 17, 2001 20:28
364 Capillary Zone Electrophoresis
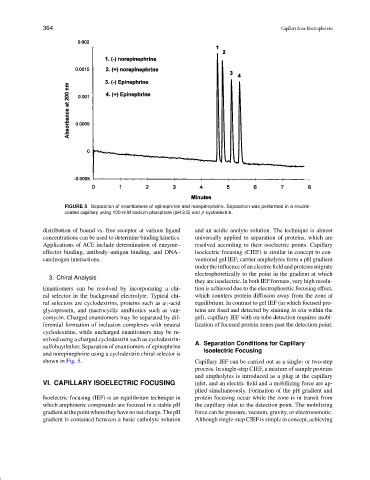
FIGURE 5 Separation of enantiomers of epinephrine and norepinephrine. Separation was performed in a neutral-
coated capillary using 100-mM sodium phosphate (pH 2.5) and β-cyclodextrin.
distribution of bound vs. free receptor at various ligand and an acidic anolyte solution. The technique is almost
concentrations can be used to determine binding kinetics. universally applied to separation of proteins, which are
Applications of ACE include determination of enzyme– resolved according to their isoelectric points. Capillary
effector binding, antibody–antigen binding, and DNA– isoelectric focusing (CIEF) is similar in concept to con-
carcinogen interactions. ventional gel IEF; carrier ampholytes form a pH gradient
under the influence of an electric field and proteins migrate
electrophoretically to the point in the gradient at which
3. Chiral Analysis
they are isoelectric. In both IEF formats, very high resolu-
Enantiomers can be resolved by incorporating a chi- tion is achieved due to the electrophoretic focusing effect,
ral selector in the background electrolyte. Typical chi- which counters protein diffusion away from the zone at
ral selectors are cyclodextrins, proteins such as α 1 -acid equilibrium. In contrast to gel IEF (in which focused pro-
glycoprotein, and macrocyclic antibiotics such as van- teins are fixed and detected by staining in situ within the
comycin. Charged enantiomers may be separated by dif- gel), capillary IEF with on-tube detection requires mobi-
ferential formation of inclusion complexes with neutral lization of focused protein zones past the detection point.
cyclodextrins, while uncharged enantiomers may be re-
solved using a charged cyclodextrin such as cyclodextrin- A. Separation Conditions for Capillary
sulfobuytlether. Separation of enantiomers of epinephrine Isoelectric Focusing
and norepinephrine using a cyclodextrin chiral selector is
shown in Fig. 5. Capillary IEF can be carried out as a single- or two-step
process. In single-step CIEF, a mixture of sample proteins
and ampholytes is introduced as a plug at the capillary
VI. CAPILLARY ISOELECTRIC FOCUSING inlet, and an electric field and a mobilizing force are ap-
plied simultaneously. Formation of the pH gradient and
Isoelectric focusing (IEF) is an equilibrium technique in protein focusing occur while the zone is in transit from
which amphoteric compounds are focused in a stable pH the capillary inlet to the detection point. The mobilizing
gradientatthepointwheretheyhavenonetcharge.ThepH force can be pressure, vacuum, gravity, or electroosmotic.
gradient is contained between a basic catholyte solution Although single-step CIEF is simple in concept, achieving