Page 105 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 105
P1: GST/MBQ P2: GQT Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009G-417 July 10, 2001 15:10
366 Membrane Structure
ing in the presence of protein, which probably arises from
slower motions.
Similar results were obtained in reconstitution experi-
ments with lipophilin and proteolipid apoprotein-lecithin
systems, sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca ,Mg -ATPase,
2+
2+
rhodopsin, and glycophorin. In all these cases deuterium
NMR revealed only one lipid population while the epr
spectra (as far as available) showed two components. The
resultsfurthershowthatproteinseitherdisorderorhavelit-
tle effect on hydrocarbon chain order in membranes above
the gel-to-liquid crystal phase transition temperature, T c ,
of the pure lipids.
The question as to how an intrinsic protein affects the
lipid environment was also investigated in systems con-
taining a relatively low amount of lipid such as in partially
delipidated cytochrome C oxidase surrounded by only 130
lipid molecules or in the crystalline lipovitellin/phosvitin
complex containing about 100 phospholipid molecules in
an interior cavity. In both systems the lipids remain in
a fluid phase. Only when the lipid pool of cytochrome
C oxidase was reduced to 6 to 18 molecules was a dis-
2
tinct broadening of the H-NMR linewidth observed,
indicating a lipid motion which was no longer axially
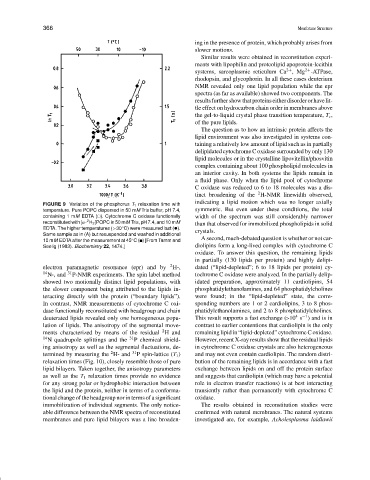
FIGURE 9 Variation of the phosphorus T 1 relaxation time with
temperature. Pure POPC dispersed in 50 mM Tris buffer, pH 7.4, symmetric. But even under these conditions, the total
containing 1 mM EDTA ( ). Cytochrome C oxidase functionally width of the spectrum was still considerably narrower
❤
2
reconstituted with [α- H 2 ]POPC in 50 mM Tris, pH 7.4, and 10 mM than that observed for immobilized phospholipids in solid
◦
EDTA. The higher temperatures (>30 C) were measured last (•). crystals.
Same sample as in (A) but resuspended and washed in additional
10 mM EDTA after the measurement at 45 C( ) [From Tamm and A second, much-debated question is whether or not car-
◦
Seelig (1983). Biochemistry 22, 1474.] diolipins form a long-lived complex with cytochrome C
oxidase. To answer this question, the remaining lipids
in partially (130 lipids per protein) and highly delipi-
electron paramagnetic resonance (epr) and by 2 H-, dated (“lipid-depleted”; 6 to 18 lipids per protein) cy-
14 31
N-, and P-NMR experiments. The spin label method tochrome C oxidase were analyzed. In the partially delip-
showed two motionally distinct lipid populations, with idated preparation, approximately 11 cardiolipins, 54
the slower component being attributed to the lipids in- phosphatidylethanolamines, and 64 phosphatidylcholines
teracting directly with the protein (“boundary lipids”). were found; in the “lipid-depleted” state, the corre-
In contrast, NMR measurements of cytochrome C oxi- sponding numbers are 1 or 2 cardiolipins, 3 to 8 phos-
dase functionally reconstituted with headgroup and chain phatidylethanolamines, and 2 to 8 phosphatidylcholines.
4
−1
deuterated lipids revealed only one homogeneous popu- This result supports a fast exchange (>10 s ) and is in
lation of lipids. The anisotropy of the segmental move- contrast to earlier contentions that cardiolipin is the only
2
ments characterized by means of the residual H and remaining lipid in “lipid-depleted” cytochrome C oxidase.
14 31
N quadrupole splittings and the P chemical shield- However, recent X-ray results show that the residual lipids
ing anisotropy as well as the segmental fluctuations, de- in cytochrome C oxidase crystals are also heterogeneous
2
termined by measuring the H- and 31 P spin-lattice (T 1 ) and may not even contain cardiolipin. The random distri-
relaxation times (Fig. 10), closely resemble those of pure bution of the remaining lipids is in accordance with a fast
lipid bilayers. Taken together, the anisotropy parameters exchange between lipids on and off the protein surface
as well as the T 1 relaxation times provide no evidence and suggests that cardiolipin (which may have a potential
for any strong polar or hydrophobic interaction between role in electron transfer reactions) is at best interacting
the lipid and the protein, neither in terms of a conforma- transiently rather than permanently with cytochrome C
tional change of the headgroup nor in terms of a significant oxidase.
immobilization of individual segments. The only notice- The results obtained in reconstitution studies were
able difference between the NMR spectra of reconstituted confirmed with natural membranes. The natural systems
membranes and pure lipid bilayers was a line broaden- investigated are, for example, Acholesplasma laidlawii