Page 12 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 12
P1: FYD Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002H-54 May 17, 2001 20:22
108 Bioenergetics
chlorophylls function only to gather light and as such they P680 are chlorophyll cation radicals and Q is a half
−
+
are often referred to as light-harvesting chlorophylls. reduced quinone and FeS is a reduced iron-sulfur pro-
−
Within picoseconds of the harvesting, the excitation en- tein. The reactions shown in Eqs. (6) and (7) cannot take
ergy is transferred to specialized chlorophyll molecules place, in the direction shown, in the dark when the re-
called reaction center chlorophylls. These reaction cen- action center chlorophylls are in the unexcited, ground
ter chlorophylls are identical to the majority of the light- state. The G for both these reactions is approximately
0
harvestingchlorophylls.Yet,ratherthanactinginapassive +24 kcal/mol. The excited reaction center chlorophylls
manner when they are excited, the reaction center chloro- are, however, much stronger reducing agents than the
phylls perform photochemistry. The two reaction center ground state chlorophylls are. The E of P700 is about
∗
0
chlorophylls are termed P700 and P680. The “P” stands 1.3 V more reducing than that of P700 in the ground state.
for pigment and the numbers refer to their absorption max- These two electron transfer reactions are the only light-
ima, in nanometers, in the red region of the spectrum. The driven reactions in photosynthesis and they set the entire
reaction center chlorophylls were first detected by light- process in motion. The electron transport chain of chloro-
induced bleaching at 680 and 700 nm. When the reac- plasts is illustrated in Fig. 10.
tion center chlorophylls are excited, either directly or by Specific light-harvesting chlorophyll–protein com-
resonance energy transfer from excited light-harvesting plexes are associated with the reaction center chlorophyll–
chlorophylls, an electron is transferred from the reaction protein complexes in assemblies known as photosystems.
center chlorophyll ensemble to an electron acceptor. These Photosystem I (PS I) contains P700 and the FeS acceptor,
light-driven oxidation–reduction reactions occur within and photosystem II (PS II), P680 and the quinone accep-
picoseconds and can operate with a quantum efficiency tor. Electron transfer in PS I generates a relatively weak
+
that is close to 100%. The reactions may be written as oxidizing agent (P700 , E =+430 mV) and a strong
0
−
follows: reductant (FeS , E =−600 mV). The primary reductant
0
generated in photosynthesis is nicotinamide adenine din-
∗
P700 + FeS → P700 + FeS − (6)
+
+
ucleotide phosphate (NADP ), which, as the name sug-
+
and gests, differs from NAD by a single phosphate. While the
+
physical properties of NADP and NAD are very similar,
+
+
∗
P680 + Q → P680 + Q , (7)
−
enzymes that use these pyridine nucleotides as substrates
where the asterisks indicate the first excited singlet state can discriminate between them by at least a factor of 1000.
+
of the reaction center chlorophyll, and FeS and Q are the In general NAD is used in catabolic metabolism as we
redox active part of an iron–sulfur protein and a quinone, have seen for glycolysis and the tricarboxylic acid cycle.
+
respectively, the first stable electron acceptors. P700 and The reduced form of NADP , NADPH, is, in contrast,
+
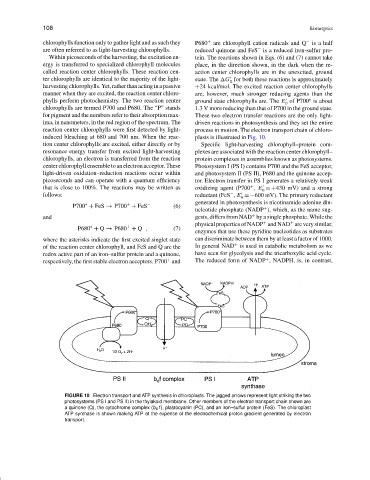
FIGURE 10 Electron transport and ATP synthesis in chloroplasts. The jagged arrows represent light striking the two
photosystems (PS I and PS II) in the thylakoid membrane. Other members of the electron transport chain shown are
a quinone (Q), the cytochrome complex (b 6 f ), plastocyanin (PC), and an iron–sulfur protein (FeS). The chloroplast
ATP synthase is shown making ATP at the expense of the electrochemical proton gradient generated by electron
transport.