Page 8 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 8
P1: FYD Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002H-54 May 17, 2001 20:22
104 Bioenergetics
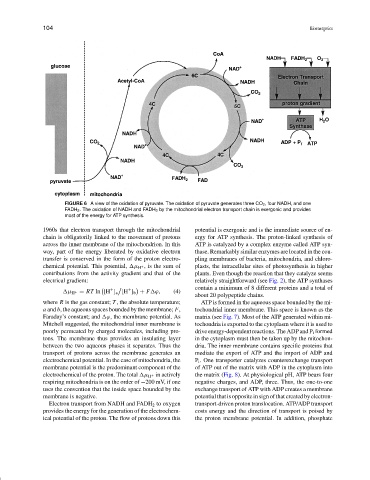
FIGURE 6 A view of the oxidation of pyruvate. The oxidation of pyruvate generates three CO 2 , four NADH, and one
FADH 2 . The oxidation of NADH and FADH 2 by the mitochondrial electron transport chain is exergonic and provides
most of the energy for ATP synthesis.
1960s that electron transport through the mitochondrial potential is exergonic and is the immediate source of en-
chain is obligatorily linked to the movement of protons ergy for ATP synthesis. The proton-linked synthesis of
across the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. In this ATP is catalyzed by a complex enzyme called ATP syn-
way, part of the energy liberated by oxidative electron thase. Remarkably similar enzymes are located in the cou-
transfer is conserved in the form of the proton electro- pling membranes of bacteria, mitochondria, and chloro-
chemical potential. This potential, µ H , is the sum of plasts, the intracellular sites of photosynthesis in higher
+
contributions from the activity gradient and that of the plants. Even though the reaction that they catalyze seems
electrical gradient: relatively straightforward (see Fig. 2), the ATP synthases
contain a minimum of 8 different proteins and a total of
µ H = RT ln [H ] a [H ] b + F ϕ, (4)
+
+
+
about 20 polypeptide chains.
where R is the gas constant; T , the absolute temperature; ATP is formed in the aqueous space bounded by the mi-
a and b, the aqueous spaces bounded by the membrane; F, tochondrial inner membrane. This space is known as the
Faraday’s constant; and ϕ, the membrane potential. As matrix (see Fig. 7). Most of the ATP generated within mi-
Mitchell suggested, the mitochondrial inner membrane is tochondria is exported to the cytoplasm where it is used to
poorly permeated by charged molecules, including pro- drive energy-dependent reactions. The ADP and P i formed
tons. The membrane thus provides an insulating layer in the cytoplasm must then be taken up by the mitochon-
between the two aqueous phases it separates. Thus the dria. The inner membrane contains specific proteins that
transport of protons across the membrane generates an mediate the export of ATP and the import of ADP and
electrochemical potential. In the case of mitochondria, the P i . One transporter catalyzes counterexchange transport
membrane potential is the predominant component of the of ATP out of the matrix with ADP in the cytoplasm into
electrochemical of the proton. The total µ H in actively the matrix (Fig. 8). At physiological pH, ATP bears four
+
respiring mitochondria is on the order of −200 mV, if one negative charges, and ADP, three. Thus, the one-to-one
uses the convention that the inside space bounded by the exchange transport of ATP with ADP creates a membrane
membrane is negative. potential that is opposite in sign of that created by electron-
Electron transport from NADH and FADH 2 to oxygen transport-driven proton translocation. ATP/ADP transport
provides the energy for the generation of the electrochem- costs energy and the direction of transport is poised by
ical potential of the proton. The flow of protons down this the proton membrane potential. In addition, phosphate