Page 4 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 4
P1: FYD Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002H-54 May 17, 2001 20:22
100 Bioenergetics
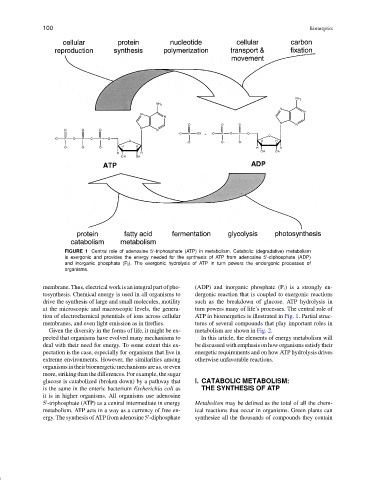
FIGURE 1 Central role of adenosine 5 -triphosphate (ATP) in metabolism. Catabolic (degradative) metabolism
is exergonic and provides the energy needed for the synthesis of ATP from adenosine 5 -diphosphate (ADP)
and inorganic phosphate (P i ). The exergonic hydrolysis of ATP in turn powers the endergonic processes of
organisms.
membrane. Thus, electrical work is an integral part of pho- (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (P i ) is a strongly en-
tosynthesis. Chemical energy is used in all organisms to dergonic reaction that is coupled to exergonic reactions
drive the synthesis of large and small molecules, motility such as the breakdown of glucose. ATP hydrolysis in
at the microscopic and macroscopic levels, the genera- turn powers many of life’s processes. The central role of
tion of electrochemical potentials of ions across cellular ATP in bioenergetics is illustrated in Fig. 1. Partial struc-
membranes, and even light emission as in fireflies. tures of several compounds that play important roles in
Given the diversity in the forms of life, it might be ex- metabolism are shown in Fig. 2.
pected that organisms have evolved many mechanisms to In this article, the elements of energy metabolism will
deal with their need for energy. To some extent this ex- be discussed with emphasis on how organisms satisfy their
pectation is the case, especially for organisms that live in energetic requirements and on how ATP hydrolysis drives
extreme environments. However, the similarities among otherwise unfavorable reactions.
organisms in their bioenergetic mechanisms are as, or even
more, striking than the differences. For example, the sugar
glucose is catabolized (broken down) by a pathway that I. CATABOLIC METABOLISM:
is the same in the enteric bacterium Escherichia coli as THE SYNTHESIS OF ATP
it is in higher organisms. All organisms use adenosine
5 -triphosphate (ATP) as a central intermediate in energy Metabolism may be defined as the total of all the chem-
metabolism. ATP acts in a way as a currency of free en- ical reactions that occur in organisms. Green plants can
ergy. The synthesis of ATP from adenosine 5 -diphosphate synthesize all the thousands of compounds they contain