Page 199 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 199
P1: GPB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN013D-617 July 27, 2001 11:42
Protein Synthesis 239
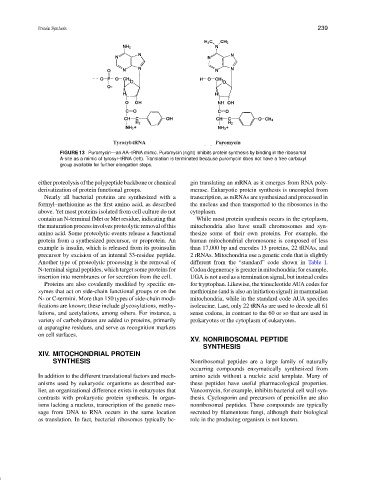
FIGURE 13 Puromycin—an AA–tRNA mimic. Puromycin (right) inhibits protein synthesis by binding in the ribosomal
A-site as a mimic of tyrosyl–tRNA (left). Translation is terminated because puromycin does not have a free carboxyl
group available for further elongation steps.
either proteolysis of the polypeptide backbone or chemical gin translating an mRNA as it emerges from RNA poly-
derivatization of protein functional groups. merase. Eukaryotic protein synthesis is uncoupled from
Nearly all bacterial proteins are synthesized with a transcription, as mRNAs are synthesized and processed in
formyl–methionine as the first amino acid, as described the nucleus and then transported to the ribosomes in the
above. Yet most proteins isolated from cell culture do not cytoplasm.
contain an N-terminal fMet or Met residue, indicating that While most protein synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm,
the maturation process involves proteolytic removal of this mitochondria also have small chromosomes and syn-
amino acid. Some proteolytic events release a functional thesize some of their own proteins. For example, the
protein from a synthesized precursor, or proprotein. An human mitochondrial chromosome is composed of less
example is insulin, which is released from its proinsulin than 17,000 bp and encodes 13 proteins, 22 tRNAs, and
precursor by excision of an internal 33-residue peptide. 2 rRNAs. Mitochondria use a genetic code that is slightly
Another type of proteolytic processing is the removal of different from the “standard” code shown in Table I.
N-terminal signal peptides, which target some proteins for Codondegeneracyisgreaterinmitochondria;forexample,
insertion into membranes or for secretion from the cell. UGA is not used as a termination signal, but instead codes
Proteins are also covalently modified by specific en- for tryptophan. Likewise, the trinucleotide AUA codes for
zymes that act on side-chain functional groups or on the methionine (and is also an initiation signal) in mammalian
N- or C-termini. More than 150 types of side-chain modi- mitochondria, while in the standard code AUA specifies
fications are known; these include glycosylations, methy- isoleucine. Last, only 22 tRNAs are used to decode all 61
lations, and acetylations, among others. For instance, a sense codons, in contrast to the 60 or so that are used in
variety of carbohydrates are added to proteins, primarily prokaryotes or the cytoplasm of eukaryotes.
at asparagine residues, and serve as recognition markers
on cell surfaces.
XV. NONRIBOSOMAL PEPTIDE
SYNTHESIS
XIV. MITOCHONDRIAL PROTEIN
SYNTHESIS Nonribosomal peptides are a large family of naturally
occurring compounds enzymatically synthesized from
In addition to the different translational factors and mech- amino acids without a nucleic acid template. Many of
anisms used by eukaryotic organisms as described ear- these peptides have useful pharmacological properties.
lier, an organizational difference exists in eukaryotes that Vancomycin, for example, inhibits bacterial cell wall syn-
contrasts with prokaryotic protein synthesis. In organ- thesis. Cyclosporin and precursors of penicillin are also
isms lacking a nucleus, transcription of the genetic mes- nonribosomal peptides. These compounds are typically
sage from DNA to RNA occurs in the same location secreted by filamentous fungi, although their biological
as translation. In fact, bacterial ribosomes typically be- role in the producing organism is not known.