Page 202 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 202
P1: GTY Final pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN017G-116 August 2, 2001 18:14
510 Vitamins and Coenzymes
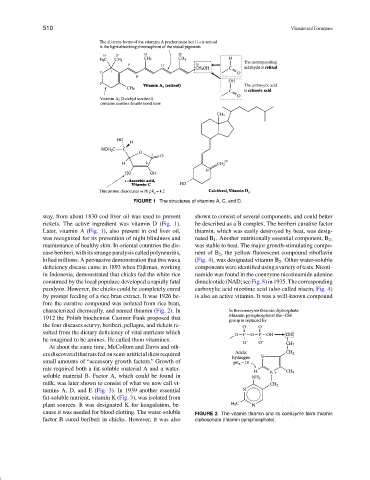
FIGURE 1 The structures of vitamins A, C, and D.
way, from about 1830 cod liver oil was used to prevent shown to consist of several components, and could better
rickets. The active ingredient was vitamin D (Fig. 1). be described as a B complex. The beriberi curative factor
Later, vitamin A (Fig. 1), also present in cod liver oil, thiamin, which was easily destroyed by heat, was desig-
was recognized for its prevention of night blindness and nated B 1 . Another nutritionally essential component, B 2 ,
maintenance of healthy skin. In oriental countries the dis- was stable to heat. The major growth-stimulating compo-
ease beriberi, with its strange paralysis called polyneuritis, nent of B 2 , the yellow fluorescent compound riboflavin
killed millions. A persuasive demonstration that this was a (Fig. 4), was designated vitamin B 2 . Other water-soluble
deficiency disease came in 1893 when Eijkman, working componentswereidentifiedusingavarietyoftests.Nicoti-
in Indonesia, demonstrated that chicks fed the white rice namide was found in the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine
consumed by the local populace developed a rapidly fatal dinucleotide(NAD;seeFig.8)in1935.Thecorresponding
paralysis. However, the chicks could be completely cured carboxylic acid nicotinic acid (also called niacin, Fig. 4)
by prompt feeding of a rice bran extract. It was 1926 be- is also an active vitamin. It was a well-known compound
fore the curative compound was isolated from rice bran,
characterized chemically, and named thiamin (Fig. 2). In
1912 the Polish biochemist Casimir Funk proposed that
the four diseases scurvy, beriberi, pellagra, and rickets re-
sulted from the dietary deficiency of vital nutrients which
he imagined to be amines. He called them vitamines.
At about the same time, McCollum and Davis and oth-
ers discovered that rats fed on semi-artificial diets required
small amounts of “accessory growth factors.” Growth of
rats required both a fat-soluble material A and a water-
soluble material B. Factor A, which could be found in
milk, was later shown to consist of what we now call vi-
tamins A, D, and E (Fig. 3). In 1939 another essential
fat-soluble nutrient, vitamin K (Fig. 3), was isolated from
plant sources. It was designated K for koagulation, be-
cause it was needed for blood clotting. The water-soluble FIGURE 2 The vitamin thiamin and its coenzyme form thiamin
factor B cured beriberi in chicks. However, it was also diphosphate (thiamin pyrophosphate).