Page 206 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 206
P1: GTY Final pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN017G-116 August 2, 2001 18:14
514 Vitamins and Coenzymes
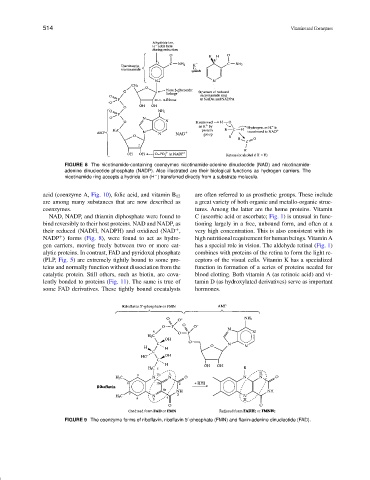
FIGURE 8 The nicotinamide-containing coenzymes nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and nicotinamide-
adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP). Also illustrated are their biological functions as hydrogen carriers. The
−
nicotinamide ring accepts a hydride ion (H ) transferred directly from a substrate molecule.
are often referred to as prosthetic groups. These include
acid (coenzyme A, Fig. 10), folic acid, and vitamin B 12
are among many substances that are now described as a great variety of both organic and metallo-organic struc-
coenzymes. tures. Among the latter are the heme proteins. Vitamin
NAD, NADP, and thiamin diphosphate were found to C (ascorbic acid or ascorbate; Fig. 1) is unusual in func-
bind reversibly to their host proteins. NAD and NADP, as tioning largely in a free, unbound form, and often at a
+
their reduced (NADH, NADPH) and oxidized (NAD , very high concentration. This is also consistent with its
NADP ) forms (Fig. 8), were found to act as hydro- high nutritional requirement for human beings. Vitamin A
+
gen carriers, moving freely between two or more cat- has a special role in vision. The aldehyde retinal (Fig. 1)
alytic proteins. In contrast, FAD and pyridoxal phosphate combines with proteins of the retina to form the light re-
(PLP, Fig. 5) are extremely tightly bound to some pro- ceptors of the visual cells. Vitamin K has a specialized
teins and normally function without dissociation from the function in formation of a series of proteins needed for
catalytic protein. Still others, such as biotin, are cova- blood clotting. Both vitamin A (as retinoic acid) and vi-
lently bonded to proteins (Fig. 11). The same is true of tamin D (as hydroxylated derivatives) serve as important
some FAD derivatives. These tightly bound cocatalysts hormones.
FIGURE 9 The coenzyme forms of riboflavin, riboflavin 5 -phosphate (FMN) and flavin-adenine dinucleotide (FAD).