Page 209 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 209
P1: GTY Final pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN017G-116 August 2, 2001 18:14
Vitamins and Coenzymes 517
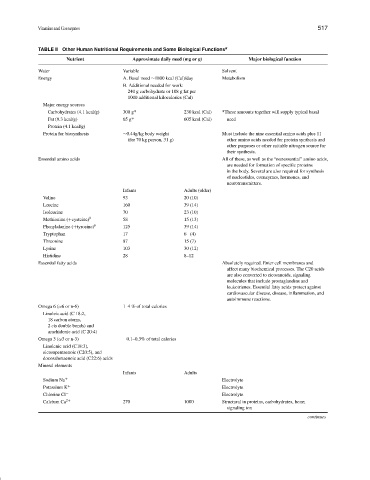
TABLE II Other Human Nutritional Requirements and Some Biological Functions a
Nutrient Approximate daily need (mg or g) Major biological function
Water Variable Solvent
Energy A. Basal need ∼1800 kcal (Cal)/day Metabolism
B. Additional needed for work:
240 g carbohydrate or 108 g fat per
1000 additional kilocalories (Cal)
Major energy sources
Carbohydrates (4.1 kcal/g) 300 g* 230 kcal (Cal) *These amounts together will supply typical basal
Fat (9.3 kcal/g) 65 g* 605 kcal (Cal) need
Protein (4.1 kcal/g)
Protein for biosynthesis ∼0.44g/kg body weight Must include the nine essential amino acids plus 11
(for 70 kg person, 31 g) other amino acids needed for protein synthesis and
other purposes or other suitable nitrogen source for
their synthesis.
Essential amino acids All of these, as well as the “nonessential” amino acids,
are needed for formation of specific proteins
in the body. Several are also required for synthesis
of nucleotides, coenzymes, hormones, and
neurotransmitters.
Infants Adults (older)
Valine 93 20 (10)
Leucine 160 39 (14)
Isoleucine 70 23 (10)
Methionine (+cysteine) b 58 15 (13)
Phenylalanine (+tyrosine) b 125 39 (14)
Tryptophan 17 6 (4)
Threonine 87 15 (7)
Lysine 103 30 (12)
Histidine 28 8–12
Essential fatty acids Absolutely required. Enter cell membranes and
affect many biochemical processes. The C20 acids
are also converted to eicosanoids, signaling
molecules that include prostaglandins and
leukotrienes. Essential fatty acids protect against
cardiovascular disease, disease, inflammation, and
autoimmune reactions.
Omega 6 (ω6 or n-6) 1–4 % of total calories
Linoleic acid (C 18:2,
18 carbon atoms,
2 cis double bonds) and
arachidonic acid (C 20:4)
Omega 3 (ω3 or n-3) 0.1–0.3% of total calories
Linolenic acid (C18:3),
eicosapentaenoic (C20:5), and
docosahexaenoic acid (C22:6) acids
Mineral elements
Infants Adults
Sodium Na + Electrolyte
Potassium K + Electrolyte
Chlorine Cl − Electrolyte
Calcium Ca 2+ 270 1000 Structural in proteins, carbohydrates, bone;
signaling ion
continues