Page 214 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 214
P1: GTY Final pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN017G-116 August 2, 2001 18:14
522 Vitamins and Coenzymes
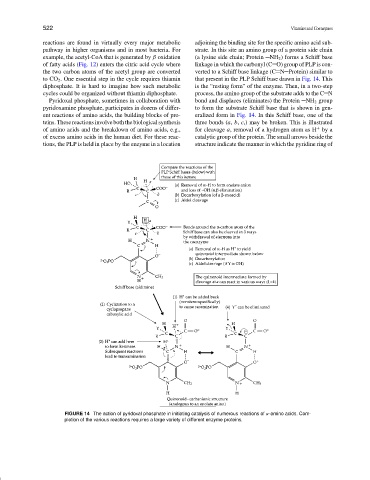
reactions are found in virtually every major metabolic adjoining the binding site for the specific amino acid sub-
pathway in higher organisms and in most bacteria. For strate. In this site an amino group of a protein side chain
example, the acetyl-CoA that is generated by β oxidation (a lysine side chain; Protein NH 2 ) forms a Schiff base
of fatty acids (Fig. 12) enters the citric acid cycle where linkage in which the carbonyl (C O) group of PLP is con-
the two carbon atoms of the acetyl group are converted verted to a Schiff base linkage (C N Protein) similar to
to CO 2 . One essential step in the cycle requires thiamin that present in the PLP Schiff base drawn in Fig. 14. This
diphosphate. It is hard to imagine how such metabolic is the “resting form” of the enzyme. Then, in a two-step
cycles could be organized without thiamin diphosphate. process, the amino group of the substrate adds to the C N
Pyridoxal phosphate, sometimes in collaboration with bond and displaces (eliminates) the Protein NH 2 group
pyridoxamine phosphate, participates in dozens of differ- to form the substrate Schiff base that is shown in gen-
ent reactions of amino acids, the building blocks of pro- eralized form in Fig. 14. In this Schiff base, one of the
teins. These reactions involve both the biological synthesis three bonds (a, b, c,) may be broken. This is illustrated
+
of amino acids and the breakdown of amino acids, e.g., for cleavage a, removal of a hydrogen atom as H by a
of excess amino acids in the human diet. For these reac- catalytic group of the protein. The small arrows beside the
tions, the PLP is held in place by the enzyme in a location structure indicate the manner in which the pyridine ring of
FIGURE 14 The action of pyridoxal phosphate in initiating catalysis of numerous reactions of α-amino acids. Com-
pletion of the various reactions requires a large variety of different enzyme proteins.