Page 217 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 217
P1: GTY Final pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN017G-116 August 2, 2001 18:14
Vitamins and Coenzymes 525
and the associated enzyme sulfite oxidase, are essential
to human life. Methane-forming bacteria create a differ-
ent complex side chain in methanopterin, which replaces
tetrahydrofolate in those organisms. Very complex pterin
derivatives form the red eye pigments of fruit flies.
E. Antioxidant Systems
Vitamins C and E, as well as ubiquinones (Fig. 3) and
derivatives of the nonmetallic element selenium, together
with sulfur-containing proteins, all participate in an elab-
orate antioxidant system. This system protects us against
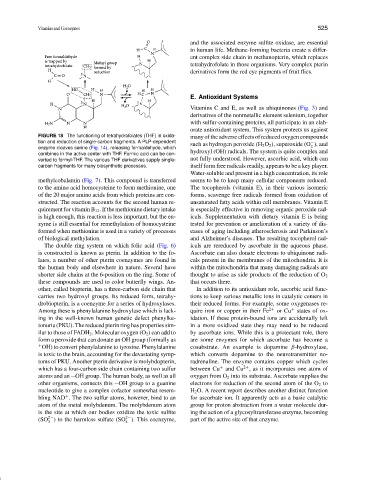
FIGURE 18 The functioning of tetrahydrofolates (THF) in oxida- many of the adverse effects of reduced oxygen compounds
tion and reduction of single-carbon fragments. A PLP-dependent −
such as hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ), superoxide (O ), and
enzyme cleaves serine (Fig. 14), releasing formaldehyde, which 2
hydroxyl (OH) radicals. The system is quite complex and
combines in the active center with THF. Formic acid can be con-
verted to formyl-THF. The various THF derivatives supply single- not fully understood. However, ascorbic acid, which can
carbon fragments for many biosynthetic processes. itself form free radicals readily, appears to be a key player.
Water-soluble and present in a high concentration, its role
methylcobalamin (Fig. 7). This compound is transferred seems to be to keep many cellular components reduced.
to the amino acid homocysteine to form methionine, one The tocopherols (vitamin E), in their various isomeric
of the 20 major amino acids from which proteins are con- forms, scavenge free radicals formed from oxidation of
structed. The reaction accounts for the second human re- unsaturated fatty acids within cell membranes. Vitamin E
quirement for vitamin B 12 . If the methionine dietary intake is especially effective in removing organic peroxide rad-
is high enough, this reaction is less important, but the en- icals. Supplementation with dietary vitamin E is being
zyme is still essential for remethylation of homocysteine tested for prevention or amelioration of a variety of dis-
formed when methionine is used in a variety of processes eases of aging including atherosclerosis and Parkinson’s
of biological methylation. and Alzheimer’s diseases. The resulting tocopherol rad-
The double ring system on which folic acid (Fig. 6) icals are rereduced by ascorbate in the aqueous phase.
is constructed is known as pterin. In addition to the fo- Ascorbate can also donate electrons to ubiquinone radi-
lates, a number of other pterin coenzymes are found in cals present in the membranes of the mitochondria. It is
the human body and elsewhere in nature. Several have within the mitochondria that many damaging radicals are
shorter side chains at the 6-position on the ring. Some of thought to arise as side products of the reduction of O 2
these compounds are used to color butterfly wings. An- that occurs there.
other, called biopterin, has a three-carbon side chain that In addition to its antioxidant role, ascorbic acid func-
carries two hydroxyl groups. Its reduced form, tetrahy- tions to keep various metallic ions in catalytic centers in
drobiopterin, is a coenzyme for a series of hydroxylases. their reduced forms. For example, some oxygenases re-
Among these is phenylalanine hydroxylase which is lack- quire iron or copper in their Fe 2+ or Cu states of ox-
+
ing in the well-known human genetic defect phenylke- idation. If these protein-bound ions are accidentally left
tonuria (PKU). The reduced pterin ring has properties sim- in a more oxidized state they may need to be reduced
ilar to those of FADH 2 . Molecular oxygen (O 2 ) can add to by ascorbate ions. While this is a protectant role, there
form a peroxide that can donate an OH group (formally as are some enzymes for which ascorbate has become a
OH) to convert phenylalanine to tyrosine. Phenylalanine cosubstrate. An example is dopamine β-hydroxylase,
+
is toxic to the brain, accounting for the devastating symp- which converts dopamine to the neurotransmitter no-
toms of PKU. Another pterin derivative is molybdopterin, radrenaline. The enzyme contains copper which cycles
which has a four-carbon side chain containing two sulfur between Cu and Cu , as it incorporates one atom of
2+
+
atoms and an OH group. The human body, as well as all oxygen from O 2 into its substrate. Ascorbate supplies the
other organisms, connects this OH group to a guanine electrons for reduction of the second atom of the O 2 to
nucleotide to give a complex cofactor somewhat resem- H 2 O. A recent report describes another distinct function
bling NAD . The two sulfur atoms, however, bind to an for ascorbate ion. It apparently acts as a basic catalytic
+
atom of the metal molybdenum. The molybdenum atom group for proton abstraction from a water molecule dur-
is the site at which our bodies oxidize the toxic sulfite ing the action of a glycosyltransferase enzyme, becoming
2−
(SO ) to the harmless sulfate (SO ). This coenzyme, part of the active site of that enzyme.
2−
3 4