Page 219 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 219
P1: GTY Final pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN017G-116 August 2, 2001 18:14
Vitamins and Coenzymes 527
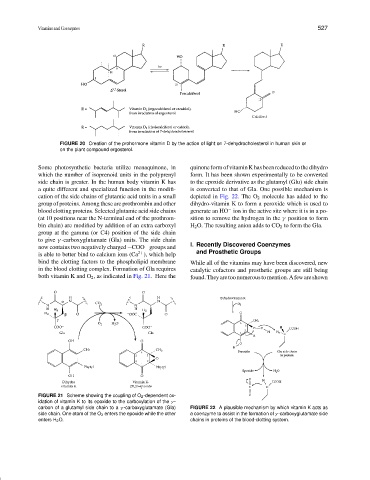
FIGURE 20 Creation of the prohormone vitamin D by the action of light on 7-dehydrocholesterol in human skin or
on the plant compound ergosterol.
Some photosynthetic bacteria utilize menaquinone, in quinone form of vitamin K has been reduced to the dihydro
which the number of isoprenoid units in the polyprenyl form. It has been shown experimentally to be converted
side chain is greater. In the human body vitamin K has to the epoxide derivative as the glutamyl (Glu) side chain
a quite different and specialized function in the modifi- is converted to that of Gla. One possible mechanism is
cation of the side chains of glutamic acid units in a small depicted in Fig. 22. The O 2 molecule has added to the
group of proteins. Among these are prothrombin and other dihydro-vitamin K to form a peroxide which is used to
−
blood clotting proteins. Selected glutamic acid side chains generate an HO ion in the active site where it is in a po-
(at 10 positions near the N-terminal end of the prothrom- sition to remove the hydrogen in the γ position to form
bin chain) are modified by addition of an extra carboxyl H 2 O. The resulting anion adds to CO 2 to form the Gla.
group at the gamma (or C4) position of the side chain
to give γ -carboxyglutamate (Gla) units. The side chain
− I. Recently Discovered Coenzymes
now contains two negatively charged COO groups and
and Prosthetic Groups
2+
is able to better bind to calcium ions (Ca ), which help
bind the clotting factors to the phospholipid membrane While all of the vitamins may have been discovered, new
in the blood clotting complex. Formation of Gla requires catalytic cofactors and prosthetic groups are still being
both vitamin K and O 2 , as indicated in Fig. 21. Here the found.Theyaretoonumeroustomention.Afewareshown
FIGURE 21 Scheme showing the coupling of O 2 -dependent ox-
idation of vitamin K to its epoxide to the carboxylation of the γ -
carbon of a glutamyl side chain to a γ -carboxyglutamate (Gla) FIGURE 22 A plausible mechanism by which vitamin K acts as
side chain. One atom of the O 2 enters the epoxide while the other a coenzyme to assist in the formation of γ -carboxyglutamate side
enters H 2 O. chains in proteins of the blood-clotting system.