Page 218 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 218
P1: GTY Final pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN017G-116 August 2, 2001 18:14
526 Vitamins and Coenzymes
F. Vitamin A and Vision nal into the 13-cis isomer within about three trillionths of
a second. In both cases, the change in shape of the retinal
While vitamin A, as retinoic acid, has important hormonal
upon absorption of light induces a small alteration in the
actions (which are not discussed here), its best known
geometry and chemical properties of the photoreceptor
function is in vision. Within photoreceptor cells of the
protein that surrounds the light-absorbing molecule. This
retina, and even in certain bacteria, vitamin A aldehyde
is enough to start a chain of signaling events in the retina
(retinal,Fig.1)formsaSchiffbasewithspecificlysineside
chains of the light receptor proteins. Two of the best known that leads to a nerve impulse being sent to the brain. In the
bacteria, the light absorption is used in a different way to
of these receptors are rhodopsin, the pigment present in the
pump a proton from the inside of the cell across the mem-
rod cells of the mammalian retina, and bacteriorhodopsin,
brane to the outside. The resulting gradient of hydrogen
the light receptor of the purple membranes of certain
ions (positive charges) across the membrane represents
salt-tolerant bacteria. In both of these cases, the protein
a store of protonic energy similar to that in an electrical
consists of a similar bundle of seven connected helical
condenser. It is used by these cells as a source of energy.
segments that pass through a membrane. The retinal Schiff
base is inside the bundle, held rigidly in a small “box.” In
both cases, a particular stereoisomer of retinal is present.
G. Vitamins A and D as Prohormones
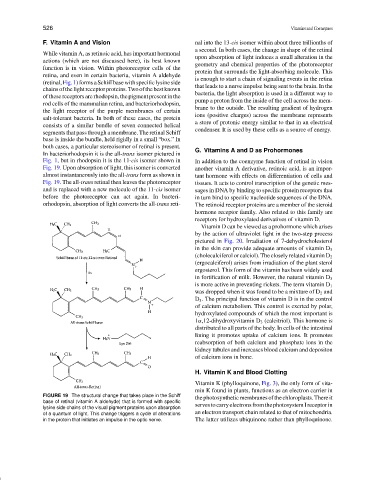
In bacteriorhodopsin it is the all-trans isomer pictured in
Fig. 1, but in rhodopsin it is the 11-cis isomer shown in In addition to the coenzyme function of retinal in vision
Fig. 19. Upon absorption of light, this isomer is converted another vitamin A derivative, retinoic acid, is an impor-
almost instantaneously into the all-trans form as shown in tant hormone with effects on differentiation of cells and
Fig. 19. The all-trans retinal then leaves the photoreceptor tissues. It acts to control transcription of the genetic mes-
and is replaced with a new molecule of the 11-cis isomer sages in DNA by binding to specific protein receptors that
before the photoreceptor can act again. In bacteri- in turn bind to specific nucleotide sequences of the DNA.
orhodopsin, absorption of light converts the all-trans reti- The retinoid receptor proteins are a member of the steroid
hormone receptor family. Also related to this family are
receptors for hydroxylated derivatives of vitamin D.
Vitamin D can be viewed as a prohormone which arises
by the action of ultraviolet light in the two-step process
pictured in Fig. 20. Irradiation of 7-dehydrocholesterol
in the skin can provide adequate amounts of vitamin D 3
(cholecalciferol or calciol). The closely related vitamin D 2
(ergocalciferol) arises from irradiation of the plant sterol
ergosterol. This form of the vitamin has been widely used
in fortification of milk. However, the natural vitamin D 3
is more active in preventing rickets. The term vitamin D 1
was dropped when it was found to be a mixture of D 2 and
D 3 . The principal function of vitamin D is in the control
of calcium metabolism. This control is exerted by polar,
hydroxylated compounds of which the most important is
1α,12-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 (calcitriol). This hormone is
distributed to all parts of the body. In cells of the intestinal
lining it promotes uptake of calcium ions. It promotes
reabsorption of both calcium and phosphate ions in the
kidney tubules and increases blood calcium and depositon
of calcium ions in bone.
H. Vitamin K and Blood Clotting
Vitamin K (phylloquinone, Fig. 3), the only form of vita-
min K found in plants, functions as an electron carrier in
FIGURE 19 The structural change that takes place in the Schiff the photosynthetic membranes of the chloroplasts. Thereit
base of retinal (vitamin A aldehyde) that is formed with specific
lysine side chains of the visual pigment proteins upon absorption servestocarryelectronsfromthephotosystemIreceptorin
of a quantum of light. This change triggers a cycle of alterations an electron transport chain related to that of mitochondria.
in the protein that initiates an impulse in the optic nerve. The latter utilizes ubiquinone rather than phylloquinone.