Page 174 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 174
P1: GKY/MBQ P2: GLQ Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology en012i-947 July 26, 2001 11:11
682 Polymers, Inorganic and Organometallic
For example, if R = R = H in ring-opening polymeriza-
tion, only chain oligomers of relatively low MW (∼1000)
are obtained. If R = CH 3 and R = H, the products are a
mixture of cyclic and chain oligomers. If R is larger than
methyl, only cyclotri- and cyclotetrasilazanes are formed
(Fig. 16B, C). Products with higher degrees of polymer-
ization are obtained by dehydrocoupling of the oligomers.
The primary use of polysilazanes is as prepolymers
in the manufacture of silicon nitride ceramics. Thus,
heating (<1000 C) the oligomers results in progressive
◦
deamination–condensation to give a cyclomatrix polymer.
Ceramic silicon nitride is formed upon further heating
(>1000 C) under vacuum. The high tensile strength cou-
◦
pled with thermal and oxidative stability of silicon nitrides
makes them useful as tough ceramic coatings or high-
impact composites in heat engine parts, power-generating FIGURE 18 Synthesis of substituted polyphosphazenes.
turbines, and machine bearings. They are also used as re-
fractorymaterialsforheat-andcorrosion-resistantjigsand
in devices where high-temperature insulation is required. prepared from PCl 5 and NH 3 (or NH 4 Cl), is then carefully
heated above 200 C to induce polymerization [Eqs. (17),
◦
(18)]:
B. Phosphorus-Based Polymers
Cl Cl
1. Polyphosphazenes
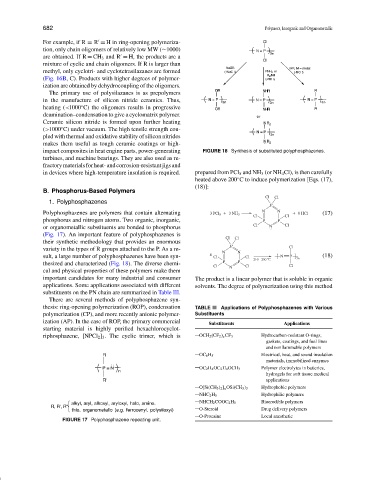
P
Polyphosphazenes are polymers that contain alternating 3 PCl 5 3 NH 3 N N 9 HCl (17)
Cl Cl
phosphorus and nitrogen atoms. Two organic, inorganic, P P
or organometallic substituents are bonded to phosphorus Cl N Cl
(Fig. 17). An important feature of polyphosphazenes is
Cl Cl
their synthetic methodology that provides an enormous
P Cl
variety in the types of R groups attached to the P. As a re- N N
sult, a large number of polyphosphazenes have been syn- n Cl Cl 210 - 250 C N P 3n (18)
thesized and characterized (Fig. 18). The diverse chemi- P P
Cl N Cl Cl
cal and physical properties of these polymers make them
important candidates for many industrial and consumer The product is a linear polymer that is soluble in organic
applications. Some applications associated with different solvents. The degree of polymerization using this method
substituents on the PN chain are summarized in Table III.
There are several methods of polyphosphazene syn-
thesis: ring-opening polymerization (ROP), condensation TABLE III Applications of Polyphosphazenes with Various
polymerization (CP), and more recently anionic polymer- Substituents
ization (AP). In the case of ROP, the primary commercial
Substituents Applications
starting material is highly purified hexachlorocyclot-
riphosphazene, [NPCl 2 ] 3 . The cyclic trimer, which is OCH 2 (CF 2 ) x CF 3 Hydrocarbon-resistant O-rings,
gaskets, coatings, and fuel lines
and nonflammable polymers
OC 6 H 5 Electrical, heat, and sound insulation
materials, immobilized enzymes
OC 2 H 4 OC 2 H 4 OCH 3 Polymer electrolytes in batteries,
hydrogels for soft tissue medical
applications
O[Si(CH 3 ) 2 ] n OSi(CH 3 ) 3 Hydrophobic polymers
NHC 2 H 5 Hydrophilic polymers
NHCH 2 COOC 2 H 5 Bioerodible polymers
O-Steroid Drug delivery polymers
O-Procaine Local anesthetic
FIGURE 17 Polyphosphazene repeating unit.