Page 177 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 177
P1: GKY/MBQ P2: GLQ Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology en012i-947 July 26, 2001 11:11
Polymers, Inorganic and Organometallic 685
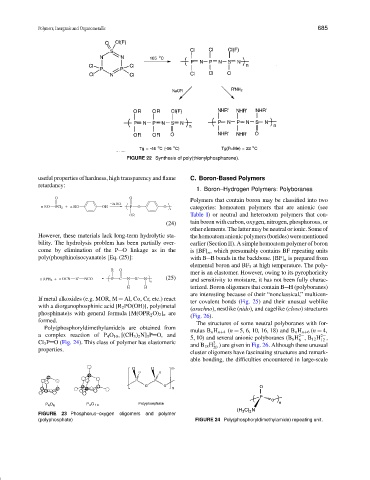
FIGURE 22 Synthesis of poly(thionylphosphazene).
useful properties of hardness, high transparency and flame C. Boron-Based Polymers
retardancy:
1. Boron–Hydrogen Polymers: Polyboranes
O O
Polymers that contain boron may be classified into two
2n HCl
n RO PCl 2 n HO OH P O O categories: homoatom polymers that are anionic (see
n
OR Table I) or neutral and heteroatom polymers that con-
(24) tain boron with carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorous, or
other elements. The latter may be neutral or ionic. Some of
However, these materials lack long-term hydrolytic sta- thehomoatomanionicpolymers(borides)werementioned
bility. The hydrolysis problem has been partially over- earlier (Section II). A simple homoatom polymer of boron
come by elimination of the P O linkage as in the is [BF] n , which presumably contains BF repeating units
poly(phosphinoisocyanate)s [Eq. (25)]: with B B bonds in the backbone. [BF] n is prepared from
elemental boron and BF 3 at high temperature. The poly-
R O
mer is an elastomer. However, owing to its pyrophoricity
n RPH 2 n OCN R′ NCO P C N R′ N (25) and sensitivity to moisture, it has not been fully charac-
n
H H terized. Boron oligomers that contain B H (polyboranes)
are interesting because of their “nonclassical,” multicen-
If metal alkoxides (e.g. MOR, M = Al, Co, Cr, etc.) react
ter covalent bonds (Fig. 25) and their unusual weblike
with a diorganophosphinic acid [R 2 PO(OH)], poly(metal
(arachno), nestlike (nido), and cagelike (closo) structures
phosphinate)s with general formula [M(OPR O) 2 ] n are (Fig. 26).
2
formed.
The structures of some neutral polyboranes with for-
Poly(phosphoryldimethylamide)s are obtained from
mulas B n H n+4 (n = 5, 6, 10, 16, 18) and B n H n+6 (n = 4,
a complex reaction of P 4 O 10 , [(CH 3 ) 2 N] 3 P O, and 2− 2−
5, 10) and several anionic polyboranes (B 6 H ,B 12 H ,
12
6
Cl 3 P O (Fig. 24). This class of polymer has elastomeric 2−
and B 18 H ) are given in Fig. 26. Although these unusual
20
properties.
cluster oligomers have fascinating structures and remark-
able bonding, the difficulties encountered in large-scale
FIGURE 23 Phosphorus–oxygen oligomers and polymer
(polyphosphate) FIGURE 24 Poly(phosphoryldimethylamide) repeating unit.