Page 98 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 98
P1: GOX/LBD P2: GLQ Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN012K-587 July 26, 2001 10:35
468 Plastics Engineering
The standard test procedures for these properties are
listed in Table III. It should be noted that, as with mechan-
ical properties, the electrical properties of plastics are not
constants. For example, the dielectric strength of a plastic
decreases as time and temperature increase.
F. Thermal Properties of Engineering Plastics
The high-temperature performance of plastics is usually
quantified by the heat-deflection test. A test sample of the
plastic is loaded in flexure and the temperature rise nec-
essary to cause a predefined deflection is measured (see
Tables I and III). The Vicat softening temperature is a sim-
ilar type of test in that the temperature at which a needle
penetrates the plastic by a prescribed amount is recorded.
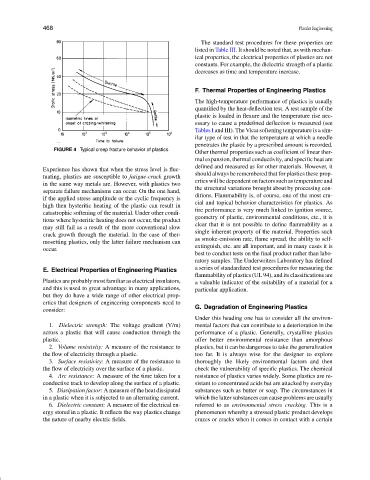
FIGURE 4 Typical creep fracture behavior of plastics.
Other thermal properties such as coefficient of linear ther-
mal expansion, thermal conductivity, and specific heat are
defined and measured as for other materials. However, it
Experience has shown that when the stress level is fluc-
should always be remembered that for plastics these prop-
tuating, plastics are susceptible to fatigue-crack growth
erties will be dependent on factors such as temperature and
in the same way metals are. However, with plastics two
the structural variations brought about by processing con-
separate failure mechanisms can occur. On the one hand,
ditions. Flammability is, of course, one of the most cru-
if the applied stress amplitude or the cyclic frequency is
cial and topical behavior characteristics for plastics. As
high then hysteritic heating of the plastic can result in
fire performance is very much linked to ignition source,
catastrophic softening of the material. Under other condi-
geometry of plastic, environmental conditions, etc., it is
tions where hysteritic heating does not occur, the product
clear that it is not possible to define flammability as a
may still fail as a result of the more conventional slow
single inherent property of the material. Properties such
crack growth through the material. In the case of ther-
as smoke-emission rate, flame spread, the ability to self-
mosetting plastics, only the latter failure mechanism can
extinguish, etc. are all important, and in many cases it is
occur.
best to conduct tests on the final product rather than labo-
ratory samples. The Underwriters Laboratory has defined
a series of standardized test procedures for measuring the
E. Electrical Properties of Engineering Plastics
flammability of plastics (UL 94), and its classifications are
Plastics are probably most familiar as electrical insulators, a valuable indicator of the suitability of a material for a
and this is used to great advantage in many applications, particular application.
but they do have a wide range of other electrical prop-
erties that designers of engineering components need to
G. Degradation of Engineering Plastics
consider:
Under this heading one has to consider all the environ-
1. Dielectric strength: The voltage gradient (V/m) mental factors that can contribute to a deterioration in the
across a plastic that will cause conduction through the performance of a plastic. Generally, crystalline plastics
plastic. offer better environmental resistance than amorphous
2. Volume resistivity: A measure of the resistance to plastics, but it can be dangerous to take the generalization
the flow of electricity through a plastic. too far. It is always wise for the designer to explore
3. Surface resistivity: A measure of the resistance to thoroughly the likely environmental factors and then
the flow of electricity over the surface of a plastic. check the vulnerability of specific plastics. The chemical
4. Arc resistance: A measure of the time taken for a resistance of plastics varies widely. Some plastics are re-
conductive track to develop along the surface of a plastic. sistant to concentrated acids but are attacked by everyday
5. Dissipation factor: A measure of the heat dissipated substances such as butter or soap. The circumstances in
in a plastic when it is subjected to an alternating current. which the latter substances can cause problems are usually
6. Dielectric constant: A measure of the electrical en- referred to as environmental stress cracking. This is a
ergy stored in a plastic. It reflects the way plastics change phenomenon whereby a stressed plastic product develops
the nature of nearby electric fields. crazes or cracks when it comes in contact with a certain