Page 99 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Polymer
P. 99
P1: GOX/LBD P2: GLQ Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN012K-587 July 26, 2001 10:35
Plastics Engineering 469
substance. Weathering is another factor that must be
taken into account. Basically, it relates to the attack on the
plastic by ultraviolet (UV) radiation, often coupled with
water absorption. Absorption of water into plastics has a
plasticizing effect that increases flexibility, but it leads to
brittleness when the water is eliminated. The UV radiation
effectively causes a breakdown of the bonds in the molec-
ular structure, and this also leads to brittleness. A loss of
color is the usual warning of weathering attack on plastics.
III. MATERIAL AND PROCESS SELECTION
It was indicated earlier that a wide range of processing
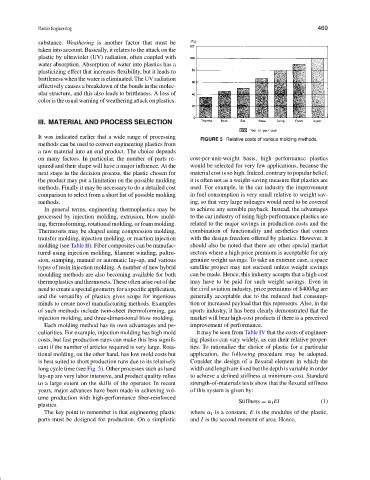
FIGURE 5 Relative costs of various molding methods.
methods can be used to convert engineering plastics from
a raw material into an end product. The choice depends
on many factors. In particular, the number of parts re- cost-per-unit-weight basis, high performance plastics
quired and their shape will have a major influence. At the would be selected for very few applications, because the
next stage in the decision process, the plastic chosen for material cost is so high. Indeed, contrary to popular belief,
the product may put a limitation on the possible molding it is often not as a weight-saving measure that plastics are
methods. Finally it may be necessary to do a detailed cost used. For example, in the car industry the improvement
comparison to select from a short list of possible molding in fuel consumption is very small relative to weight sav-
methods. ing, so that very large mileages would need to be covered
In general terms, engineering thermoplastics may be to achieve any sensible payback. Instead, the advantages
processed by injection molding, extrusion, blow mold- to the car industry of using high-performance plastics are
ing, thermoforming, rotational molding, or foam molding. related to the major savings in production costs and the
Thermosets may be shaped using compression molding, combination of functionality and aesthetics that comes
transfer molding, injection molding, or reaction injection with the design freedom offered by plastics. However, it
molding (see Table II). Fiber composites can be manufac- should also be noted that there are other special market
tured using injection molding, filament winding, pultru- sectors where a high price premium is acceptable for any
sion, stamping, manual or automatic lay-up, and various genuine weight savings. To take an extreme case, a space
types of resin injection molding. A number of new hybrid satellite project may not succeed unless weight savings
moulding methods are also becoming available for both can be made. Hence, this industry accepts that a high cost
thermoplastics and thermosets. These often arise out of the may have to be paid for such weight savings. Even in
need to create a special geometry for a specific application, the civil aviation industry, price premiums of $400/kg are
and the versatility of plastics gives scope for ingenious generally acceptable due to the reduced fuel consump-
minds to create novel manufacturing methods. Examples tion or increased payload that this represents. Also, in the
of such methods include twin-sheet thermoforming, gas sports industry, it has been clearly demonstrated that the
injection molding, and three-dimensional blow molding. market will bear high-cost products if there is a perceived
Each molding method has its own advantages and pe- improvement of performance.
culiarities. For example, injection molding has high mold It may be seen from Table IV that the costs of engineer-
costs, but fast production rates can make this less signifi- ing plastics can vary widely, as can their relative proper-
cant if the number of articles required is very large. Rota- ties. To rationalize the choice of plastic for a particular
tional molding, on the other hand, has low mold costs but application, the following procedure may be adopted.
is best suited to short production runs due to its relatively Consider the design of a flexural element in which the
long cycle time (see Fig. 5). Other processes such as hand width and length are fixed but the depth is variable in order
lay-up are very labor intensive, and product quality relies to achieve a defined stiffness at minimum cost. Standard
to a large extent on the skills of the operator. In recent strength-of-materials texts show that the flexural stiffness
years, major advances have been made in achieving vol- of this system is given by:
ume production with high-performance fiber-reinforced
Stiffness = α 1 EI (1)
plastics.
The key point to remember is that engineering plastic where α 1 is a constant, E is the modulus of the plastic,
parts must be designed for production. On a simplistic and I is the second moment of area. Hence,