Page 12 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 12
P1: FYK Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN001F-11 May 7, 2001 12:19
220 Actinide Elements
To obtain and stabilize the actinides under study in the lap as for the transition elements. The energies of the 5 f ,
elemental/metallic state, the reduction of actinide oxides 6d,7s, and 7p orbitals are comparable over a range of
with lanthanum metal and the desorption of actinide atoms atomic numbers, and since the orbitals overlap spatially,
from metals like tantalum, titanium, and zirconium have bonding can involve any or all of them. This is especially
been applied successfully. important in the first half of the actinide series. Oxidation
states up to +7 are available, and the electronic structure
of an actinide in any given oxidation state may vary from
B. Properties of Actinide Metals compound to compound and in solution, depending on the
ligands, because the small differences in energy between
1. Electronic Structure
the 5 f ,6d,7s, and 7p orbitals can be compensated within
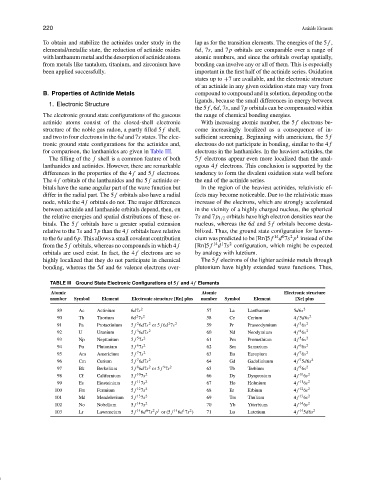
The electronic ground state configurations of the gaseous the range of chemical bonding energies.
actinide atoms consist of the closed-shell electronic With increasing atomic number, the 5 f electrons be-
structure of the noble gas radon, a partly filled 5 f shell, come increasingly localized as a consequence of in-
and two to four electrons in the 6d and 7s states. The elec- sufficient screening. Beginning with americium, the 5 f
tronic ground state configurations for the actinides and, electrons do not participate in bonding, similar to the 4 f
for comparison, the lanthanides are given in Table III. electrons in the lanthanides. In the heaviest actinides, the
The filling of the f shell is a common feature of both 5 f electrons appear even more localized than the anal-
lanthanides and actinides. However, there are remarkable ogous 4 f electrons. This conclusion is supported by the
differences in the properties of the 4 f and 5 f electrons. tendency to form the divalent oxidation state well before
The 4 f orbitals of the lanthanides and the 5 f actinide or- the end of the actinide series.
bitals have the same angular part of the wave function but In the region of the heaviest actinides, relativistic ef-
differ in the radial part. The 5 f orbitals also have a radial fects may become noticeable. Due to the relativistic mass
node, while the 4 f orbitals do not. The major differences increase of the electrons, which are strongly accelerated
between actinide and lanthanide orbitals depend, then, on in the vicinity of a highly charged nucleus, the spherical
the relative energies and spatial distributions of these or- 7s and 7p 1/2 orbitals have high electron densities near the
bitals. The 5 f orbitals have a greater spatial extension nucleus, whereas the 6d and 5 f orbitals become desta-
relative to the 7s and 7p than the 4 f orbitals have relative bilized. Thus, the ground state configuration for lawren-
2 1
14 0
to the 6s and 6p. This allows a small covalent contribution cium was predicted to be [Rn]5 f d 7s p instead of the
2
14 1
from the 5 f orbitals, whereas no compounds in which 4 f [Rn]5 f d 7s configuration, which might be expected
orbitals are used exist. In fact, the 4 f electrons are so by analogy with lutetium.
highly localized that they do not participate in chemical The 5 f electrons of the lighter actinide metals through
bonding, whereas the 5d and 6s valence electrons over- plutonium have highly extended wave functions. Thus,
TABLE III Ground State Electronic Configurations of 5 f and 4 f Elements
Atomic Atomic Electronic structure
number Symbol Element Electronic structure [Rn] plus number Symbol Element [Xe] plus
89 Ac Actinium 6d7s 2 57 La Lanthanum 5d6s 2
2
90 Th Thorium 6d 7s 2 58 Ce Cerium 4 f 5d6s 2
3
2
2
2
91 Pa Protactinium 5 f 6d7s or 5 f 6d 7s 2 59 Pr Praseodymium 4 f 6s 2
4
3
92 U Uranium 5 f 6d7s 2 60 Nd Neodymium 4 f 6s 2
5
5
93 Np Neptunium 5 f 7s 2 61 Pm Promethium 4 f 6s 2
6
6
94 Pu Plutonium 5 f 7s 2 62 Sm Samarium 4 f 6s 2
7
7
95 Am Americium 5 f 7s 2 63 Eu Europium 4 f 6s 2
7
7
96 Cm Curium 5 f 6d7s 2 64 Gd Gadoliniuum 4 f 5d6s 2
9
8
2
9
97 Bk Berkelium 5 f 6d7s or 5 f 7s 2 65 Tb Terbium 4 f 6s 2
98 Cf Californium 5 f 10 7s 2 66 Dy Dysprosium 4 f 10 6s 2
99 Es Einsteinium 5 f 11 7s 2 67 Ho Holmium 4 f 11 6s 2
100 Fm Fermium 5 f 12 7s 2 68 Er Erbium 4 f 12 6s 2
101 Md Mendelevium 5 f 13 7s 2 69 Tm Thulium 4 f 13 6s 2
102 No Nobelium 5 f 14 7s 2 70 Yb Ytterbium 4 f 14 6s 2
2
1
0
2 1
103 Lr Lawrencium 5 f 14 6d 7s p or (5 f 14 6d 7s ) 71 Lu Lutetium 4 f 14 5d6s 2