Page 14 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 14
P1: FYK Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN001F-11 May 7, 2001 12:19
222 Actinide Elements
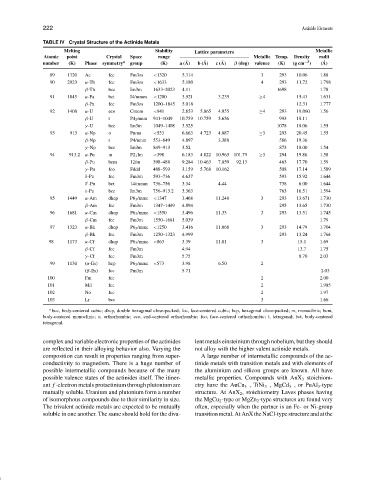
TABLE IV Crystal Structure of the Actinide Metals
Melting Stability Lattice parameters Metallic
Atomic point Crystal Space range Metallic Temp. Density radii
number (K) Phase symmetry a group (K) a ( ˚ A) b ( ˚ A) c ( ˚ A) β (deg) valence (K) (g cm −3 ) ( ˚ A)
89 1320 Ac fcc Fm3m <1320 5.314 3 293 10.06 1.88
90 2023 α-Th fcc Fm3m <1633 5.180 4 293 11.72 1.798
β-Th bcc Im3m 1633–2023 4.11 1698 1.78
91 1845 α-Pa bct I4/mmm <1200 3.921 3.235 ≥4 15.43 1.631
β-Pa fcc Fm3m 1200–1845 5.018 12.31 1.777
92 1408 α-U eco Cmcm <941 2.853 5.865 4.955 ≥4 293 19.060 1.56
β-U t P4 2 mnm 941–1049 10.759 10.759 5.656 993 18.11
γ -U bcc Im3m 1049–1408 3.525 1078 18.06 1.55
93 913 α-Np o Pnma <553 6.663 4.723 4.887 ≥3 293 20.45 1.55
β-Np t P4/nmm 553–849 4.897 3.388 586 19.36
γ -Np bcc Im3m 849–913 3.52 873 18.00 1.54
94 913.2 α-Pu m P2 1 Im <398 6.183 4.822 10.963 101.79 ≥3 294 19.86 1.58
β-Pu bcm 12/m 398–488 9.284 10.463 7.859 92.13 463 17.70 1.59
γ -Pu fco Fddd 488–593 3.159 5.768 10.162 508 17.14 1.589
δ-Pu fcc Fm3m 593–736 4.637 593 15.92 1.644
δ -Pu bct 14/mmm 736–756 3.34 4.44 738 6.00 1.644
ε-Pu bcc Im3m 756–913.2 3.363 763 16.51 1.594
95 1449 α-Am dhcp P6 3 /mmc <1347 3.468 11.248 3 293 13.671 1.730
β-Am fcc Fm3m 1347–1449 4.894 295 13.65 1.730
96 1681 α-Cm dhcp P6 3 /mmc <1550 3.496 11.33 3 293 13.51 1.745
β-Cm fcc Fm3m 1550–1681 5.039 1.79
97 1323 α-Bk dhcp P6 3 /mmc <1250 3.416 11.068 3 293 14.79 1.704
β-Bk fcc Fm3m 1250–1323 4.999 293 13.24 1.764
98 1173 α-Cf dhcp P6 3 /mmc <863 3.39 11.01 3 15.1 1.69
β-Cf fcc Fm3m 4.94 13.7 1.75
γ -Cf fcc Fm3m 5.75 8.70 2.03
99 1130 (α-Es) hcp P6 3 /mmc <573 3.98 6.50 2
(β-Es) fcc Fm3m 5.71 2.03
100 Fm fcc 2 2.00
101 Md fcc 2 1.985
102 No fcc 2 1.97
103 Lr bcc 3 1.66
a bcc, body-centered cubic; dhcp, double hexagonal close-packed; fcc, face-centered cubic; hcp, hexagonal close-packed; m, monoclinic; bcm,
body-centered monoclinic; o, orthorhombic; eco, end-centered orthorhombic; fco, face-centered orthorhombic; t, tetragonal; bct, body-centered
tetragonal.
complex and variable electronic properties of the actinides lent metals einsteinium through nobelium, but they should
are reflected in their alloying behavior also. Varying the not alloy with the higher valent actinide metals.
composition can result in properties ranging from super- A large number of intermetallic compounds of the ac-
conductivity to magnetism. There is a huge number of tinide metals with transition metals and with elements of
possible intermetallic compounds because of the many the aluminium and silicon groups are known. All have
possible valence states of the actinides itself. The itiner- metallic properties. Compounds with AnX 3 stoichiom-
ant f -electron metals protactinium through plutonium are etry have the AuCu 3 , TiNi 3 , MgCd 3 , or PuAl 3 -type
−
−
−
mutually soluble. Uranium and plutonium form a number structure. At AnX 2 , stoichiometry Laves phases having
of isomorphous compounds due to their similarity in size. the MgCu 2 -type or MgZn 2 -type structures are found very
The trivalent actinide metals are expected to be mutually often, especially when the partner is an Fe- or Ni-group
soluble in one another. The same should hold for the diva- transitionmetal.AtAnXtheNaCl-typestructureandatthe