Page 193 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 193
P1: GSS Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009F-398 July 6, 2001 20:34
2 Main Group Elements
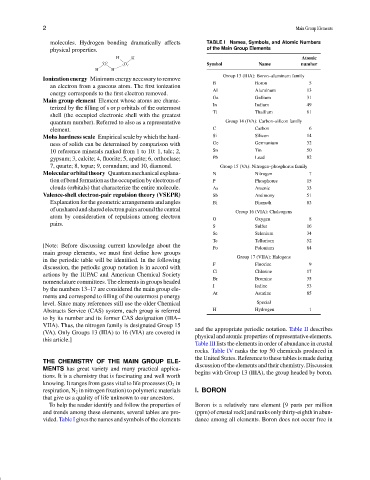
molecules. Hydrogen bonding dramatically affects TABLE I Names, Symbols, and Atomic Numbers
physical properties. of the Main Group Elements
H H Atomic
O O Symbol Name number
H H
Group 13 (IIIA): Boron–aluminum family
Ionization energy Minimum energy necessary to remove
B Boron 5
an electron from a gaseous atom. The first ionization
Al Aluminum 13
energy corresponds to the first electron removed.
Ga Gallium 31
Main group element Element whose atoms are charac-
In Indium 49
terized by the filling of s or p orbitals of the outermost
Tl Thallium 81
shell (the occupied electronic shell with the greatest
quantum number). Referred to also as a representative Group 14 (IVA): Carbon–silicon family
element. C Carbon 6
Mohs hardness scale Empirical scale by which the hard- Si Silicon 14
ness of solids can be determined by comparison with Ge Germanium 32
10 reference minerals ranked from 1 to 10: 1, talc; 2, Sn Tin 50
gypsum; 3, calcite; 4, fluorite; 5, apatite; 6, orthoclase; Pb Lead 82
7, quartz; 8, topaz; 9, corundum; and 10, diamond. Group 15 (VA): Nitrogen–phosphorus family
Molecularorbitaltheory Quantummechanicalexplana- N Nitrogen 7
tion of bond formation as the occupation by electrons of P Phosphorus 15
clouds (orbitals) that characterize the entire molecule. As Arsenic 33
Valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory (VSEPR) Sb Antimony 51
Explanation for the geometric arrangements and angles Bi Bismuth 83
of unshared and shared electron pairs around the central
Group 16 (VIA): Chalcogens
atom by consideration of repulsions among electron
O Oxygen 8
pairs.
S Sulfur 16
Se Selenium 34
Te Tellurium 52
[Note: Before discussing current knowledge about the
Po Polonium 84
main group elements, we must first define how groups
Group 17 (VIIA): Halogens
in the periodic table will be identified. In the following
F Fluorine 9
discussion, the periodic group notation is in accord with
Cl Chlorine 17
actions by the IUPAC and American Chemical Society
Br Bromine 35
nomenclature committees. The elements in groups headed
I Iodine 53
by the numbers 13–17 are considered the main group ele-
At Astatine 85
ments and correspond to filling of the outermost p energy
level. Since many references still use the older Chemical Special
Abstracts Service (CAS) system, each group is referred H Hydrogen 1
to by its number and its former CAS designation (IIIA–
VIIA). Thus, the nitrogen family is designated Group 15
and the appropriate periodic notation. Table II describes
(VA). Only Groups 13 (IIIA) to 16 (VIA) are covered in
physical and atomic properties of representative elements.
this article.]
Table III lists the elements in order of abundance in crustal
rocks. Table IV ranks the top 50 chemicals produced in
the United States. Reference to these tables is made during
THE CHEMISTRY OF THE MAIN GROUP ELE-
discussion of the elements and their chemistry. Discussion
MENTS has great variety and many practical applica-
begins with Group 13 (IIIA), the group headed by boron.
tions. It is a chemistry that is fascinating and well worth
knowing. It ranges from gases vital to life processes (O 2 in
respiration, N 2 in nitrogen fixation) to polymeric materials I. BORON
that give us a quality of life unknown to our ancestors.
To help the reader identify and follow the properties of Boron is a relatively rare element [9 parts per million
and trends among these elements, several tables are pro- (ppm)ofcrustalrock]andranksonlythirty-eighthinabun-
vided. Table I gives the names and symbols of the elements dance among all elements. Boron does not occur free in